Expression of apoptosis-regulating genes in the rat prostate following botulinum toxin type A injection
- PMID: 22216975
- PMCID: PMC3265407
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-12-1
Expression of apoptosis-regulating genes in the rat prostate following botulinum toxin type A injection
Abstract
Background: Onabotulinumtoxin A (OnabotA) injection has been investigated as a novel treatment for benign prostatic enlargement caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. An OnabotA-induced volume reduction caused by sympathetic fibers impairment has been proposed as a potential mechanism of action. Our aim was to investigate the expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in the rat prostate following OnabotA intraprostatic injection.
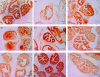
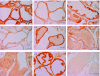
Methods: Adult Wistar rats were injected in the ventral lobes of the prostate with 10 U of OnabotA or saline. A set of OnabotA-injected animals was further treated with 0.5 mg/kg of phenylephrine (PHE) subcutaneously daily. All animals were sacrificed after 1 week and had their prostates harvested. Immunohistochemical staining was performed for Bax, Bcl-xL and caspase-3 proteins and visualized by the avidin-biotin method. The optical density of the glandular cells was also determined, with measurement of differences between average optical densities for each group.
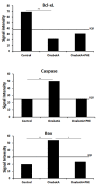
Results: Saline-treated animals showed intense epithelial staining for Bcl-xL and a faint labelling for both Bax and Caspase-3. OnabotA-treated rats showed a reduced epithelial staining of Bcl-xL and a consistently increased Bax and Caspase-3 staining when compared with saline-treated animals. PHE-treated animals showed a stronger Bcl-xL staining and reduced staining of both Bax and Caspase-3 when compared to the OnabotA group. Mean signal intensity measurements for each immunoreaction confirmed a significant decrease of the signal intensity for Bcl-xL and a significant increase of the signal intensity for Bax and Caspase 3 in OnabotA-injected animals when compared with the control group. In OnabotA+PHE treated animals mean signal intensity for Bcl-xL, Bax and Caspase 3 immunoreactions was identical to that of the control animals.
Conclusions: These results support the hypothesis that OnabotA activates apoptotic pathways in the rat prostate through a mechanism that involves sympathetic outflow impairment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of prostate atrophy after glandular botulinum neurotoxin type a injection: an experimental study in the rat.Eur Urol. 2009 Jul;56(1):134-40. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Eur Urol. 2009. PMID: 18649990
-
Ganoderma spore lipid inhibits N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced retinal photoreceptor apoptosis in vivo.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Mar;90(3):397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.11.017. Epub 2009 Dec 7. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20003911
-
Influence of Onabotulinumtoxin A on testes of the growing rat.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016 Dec;30(12):608-613. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21828. Epub 2016 Aug 5. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27492265
-
[Effects of intraprostatic injection of botulinum toxin A (BTX-A) on benign prostate hyperplasia].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2010 Oct;16(10):905-10. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2010. PMID: 21243754 Chinese.
-
T-2 toxin-induced apoptosis involving Fas, p53, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, Bax and caspase-3 signaling pathways in human chondrocytes.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008 Jun;9(6):455-63. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0820013. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008. PMID: 18543398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Proteinaceous Compounds With Multiple Activities Toward Cancers and Microbial Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Aug 6;10:1690. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01690. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31447795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifestyle recommendations and pelvic floor muscle training with Knack maneuver for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a randomized controlled trial.Support Care Cancer. 2025 Jan 31;33(2):132. doi: 10.1007/s00520-025-09197-z. Support Care Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39888446 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanism of Action of Botulinum Toxin A in Treatment of Functional Urological Disorders.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;12(2):129. doi: 10.3390/toxins12020129. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxic potential of botulinum toxin type A on senescence in a Drosophila melanogaster model.Toxicol Rep. 2021 Aug 16;8:1576-1582. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.08.002. eCollection 2021. Toxicol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34458104 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic action of botulinum toxin on masseter muscle in rats: early and late changes in the expression of molecular markers.Springerplus. 2016 Jul 7;5(1):991. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2680-9. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27398270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Silva J, Silva C, Saraiva L, Silva A, Pinto R, Dinis P, Cruz F. Intraprostatic botulinum toxin type A injection in patients unfit for surgery presenting with refractory urinary retention and benign prostatic enlargement. Effect on prostate volume and micturition resumption. Eur Urol. 2008;53:153–159. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.08.050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

