Endotoxin-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in the HIV-1 transgenic rat
- PMID: 22216977
- PMCID: PMC3322344
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-3
Endotoxin-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in the HIV-1 transgenic rat
Abstract
Background: Repeated exposure to a low dose of a bacterial endotoxin such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) causes immune cells to become refractory to a subsequent endotoxin challenge, a phenomenon known as endotoxin tolerance (ET). During ET, there is an imbalance in pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production, leading to a dysregulated immune response. HIV-1 viral proteins are known to have an adverse effect on the immune system. However, the effects of HIV-1 viral proteins during ET have not been investigated.
Methods: In this study, HIV-1 transgenic (HIV-1Tg) rats and control F344 rats (n = 12 ea) were randomly treated with 2 non-pyrogenic doses of LPS (LL) to induce ET, or saline (SS), followed by a high challenge dose of LPS (LL+L, SS+L) or saline (LL+S, SS+S). The gene expression of 84 cytokines, chemokines, and their receptors in the brain and spleen was examined by relative quantitative PCR using a PCR array, and protein levels in the brain, spleen, and serum of 7 of these 84 genes was determined using an electrochemiluminescent assay.
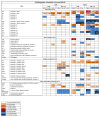
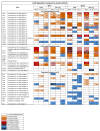
Results: In the spleen, there was an increase in key pro-inflammatory (IL1α, IL-1β, IFN-γ) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines, and inflammatory chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl7, and Ccl9,) in response to LPS in the SS+L and LL+L (ET) groups of both the HIV-1Tg and F344 rats, but was greater in the HIV-1Tg rats than in the F344. In the ET HIV-1Tg and F344 (LL+L) rats in the spleen, the LPS-induced increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines was diminished and that of the anti-inflammatory cytokine was enhanced compared to the SS+L group rats. In the brain, IL-1β, as well as the Ccl2, Ccl3, and Ccl7 chemokines were increased to a greater extent in the HIV-1Tg rats compared to the F344; whereas Cxcl1, Cxcl10, and Cxcl11 were increased to a greater extent in the F344 rats compared to the HIV-1Tg rats in the LL+L and SS+L groups.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that the continuous presence of HIV-1 viral proteins can have tissue-dependent effects on endotoxin-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in the ET state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation Effect of HIV-1 Viral Proteins and Nicotine on Expression of the Immune-Related Genes in Brain of the HIV-1 Transgenic Rats.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;11(3):562-71. doi: 10.1007/s11481-016-9679-4. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27147085 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 transgenic rats display alterations in immunophenotype and cellular responses associated with aging.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 15;9(8):e105256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105256. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25127062 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of docosahexaenoic acid on locomotor activity in ethanol-treated HIV-1 transgenic rats.J Neurovirol. 2018 Feb;24(1):88-97. doi: 10.1007/s13365-017-0597-x. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Neurovirol. 2018. PMID: 29260441 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and ethanol concentration-dependent effects of acute binge drinking in the HIV-1 transgenic rat.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Jan;37 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):E70-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01860.x. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 22823339 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the modulation of an LPS-induced inflammatory response during morphine tolerance.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013 Sep 1;132(1-2):38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.12.022. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013. PMID: 23352192
Cited by
-
NLRP12 Inflammasome Expression in the Rat Brain in Response to LPS during Morphine Tolerance.Brain Sci. 2017 Feb 6;7(2):14. doi: 10.3390/brainsci7020014. Brain Sci. 2017. PMID: 28178176 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation Effect of HIV-1 Viral Proteins and Nicotine on Expression of the Immune-Related Genes in Brain of the HIV-1 Transgenic Rats.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;11(3):562-71. doi: 10.1007/s11481-016-9679-4. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27147085 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV-1 transgenic rat model of neuroHIV.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Aug;48:336-49. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25733103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV and symptoms of depression are independently associated with impaired glucocorticoid signaling.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Oct;96:118-125. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29936334 Free PMC article.
-
CPI-637 as a Potential Bifunctional Latency-Reversing Agent That Targets Both the BRD4 and TIP60 Proteins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 19;11:686035. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.686035. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34350133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenberger CM, Scott MG, Gold MR, Hancock RE, Finlay BB. Salmonella typhimurium infection and lipopolysaccharide stimulation induce similar changes in macrophage gene expression. J Immunol. 2000;164:5894–5904. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull AV, Rivier CL. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources