Controversies in modern evolutionary biology: the imperative for error detection and quality control
- PMID: 22217008
- PMCID: PMC3311146
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-5
Controversies in modern evolutionary biology: the imperative for error detection and quality control
Abstract
Background: The data from high throughput genomics technologies provide unique opportunities for studies of complex biological systems, but also pose many new challenges. The shift to the genome scale in evolutionary biology, for example, has led to many interesting, but often controversial studies. It has been suggested that part of the conflict may be due to errors in the initial sequences. Most gene sequences are predicted by bioinformatics programs and a number of quality issues have been raised, concerning DNA sequencing errors or badly predicted coding regions, particularly in eukaryotes.
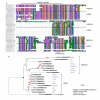
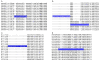
Results: We investigated the impact of these errors on evolutionary studies and specifically on the identification of important genetic events. We focused on the detection of asymmetric evolution after duplication, which has been the subject of controversy recently. Using the human genome as a reference, we established a reliable set of 688 duplicated genes in 13 complete vertebrate genomes, where significantly different evolutionary rates are observed. We estimated the rates at which protein sequence errors occur and are accumulated in the higher-level analyses. We showed that the majority of the detected events (57%) are in fact artifacts due to the putative erroneous sequences and that these artifacts are sufficient to mask the true functional significance of the events.
Conclusions: Initial errors are accumulated throughout the evolutionary analysis, generating artificially high rates of event predictions and leading to substantial uncertainty in the conclusions. This study emphasizes the urgent need for error detection and quality control strategies in order to efficiently extract knowledge from the new genome data.
© 2012 Prosdocimi et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Analysis, identification and correction of some errors of model refseqs appeared in NCBI Human Gene Database by in silico cloning and experimental verification of novel human genes].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004 May;31(5):431-43. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15478601 Chinese.
-
Targeted sequencing for high-resolution evolutionary analyses following genome duplication in salmonid fish: Proof of concept for key components of the insulin-like growth factor axis.Mar Genomics. 2016 Dec;30:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2016.06.003. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Mar Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27346185
-
A case for evolutionary genomics and the comprehensive examination of sequence biodiversity.Mol Biol Evol. 2000 Dec;17(12):1776-88. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026278. Mol Biol Evol. 2000. PMID: 11110893 Review.
-
Evolution of vertebrate genes related to prion and Shadoo proteins--clues from comparative genomic analysis.Mol Biol Evol. 2004 Dec;21(12):2210-31. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh245. Epub 2004 Sep 1. Mol Biol Evol. 2004. PMID: 15342797
-
Functional inferences from reconstructed evolutionary biology involving rectified databases--an evolutionarily grounded approach to functional genomics.Res Microbiol. 2000 Mar;151(2):97-106. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(00)00123-6. Res Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10865954 Review.
Cited by
-
Advantages of an Improved Rhesus Macaque Genome for Evolutionary Analyses.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 2;11(12):e0167376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167376. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27911958 Free PMC article.
-
LEON-BIS: multiple alignment evaluation of sequence neighbours using a Bayesian inference system.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Jul 7;17(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1146-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27387560 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of eutherian fibroblast growth factor genes.BMC Genomics. 2020 Aug 5;21(1):542. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06958-4. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32758140 Free PMC article.
-
The Ancient History of Peptidyl Transferase Center Formation as Told by Conservation and Information Analyses.Life (Basel). 2020 Aug 5;10(8):134. doi: 10.3390/life10080134. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32764248 Free PMC article.
-
Allostery Wiring Map for Kinesin Energy Transduction and Its Evolution.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 30;291(40):20932-20945. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.733675. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27507814 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

