Surveillance in Eastern India (2007-2009) revealed reassortment event involving NS and PB1-F2 gene segments among co-circulating influenza A subtypes
- PMID: 22217077
- PMCID: PMC3284387
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-3
Surveillance in Eastern India (2007-2009) revealed reassortment event involving NS and PB1-F2 gene segments among co-circulating influenza A subtypes
Abstract
Background: Influenza A virus encodes for eleven proteins, of which HA, NA, NS1 and PB1-F2 have been implicated in viral pathogenicity and virulence. Thus, in addition to the HA and NA gene segments, monitoring diversity of NS1 and PB1-F2 is also important.
Methods: 55 out of 166 circulating influenza A strains (31 H1N1 and 24 H3N2) were randomly picked during 2007-2009 and NS and PB1-F2 genes were sequenced. Phylogenetic analysis was carried out with reference to the prototype strains, concurrent vaccine strains and other reference strains isolated world wide.
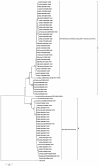
Results: Comparative analysis of both nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences, revealed presence of NS gene with A/PR/8/34(H1N1)-like mutations (H4N, Q21R, A22V, K44R, N53D, C59R, V60A, F103S and M106I) in both RNA-binding and effector domain of NS1 protein, and G63E, the HPAI-H5N1-like mutation in NEP/NS2 of five A/H1N1 strains of 2007 and 2009. NS1 of other A/H1N1 strains clustered with concurrent A/H1N1 vaccine strains. Of 31 A/H1N1 strains, five had PB1-F2 similar to the H3N2 strains; six had non-functional PB1-F2 protein (11 amino acids) similar to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 strains and rest 20 strains had 57 amino acids PB1-F2 protein, similar to concurrent A/H1N1 vaccine strain. Interestingly, three A/H1N1 strains with H3N2-like PB1-F2 protein carried primitive PR8-like NS gene. Full gene sequencing of PB1 gene confirmed presence of H3N2-like PB1 gene in these A/H1N1 strains.
Conclusion: Overall the study highlights reassortment event involving gene segments other than HA and NA in the co-circulating A/H1N1 and A/H3N2 strains and their importance in complexity of influenza virus genetics. In contrast, NS and PB1-F2 genes of all A/H3N2 eastern India strains were highly conserved and homologous to the concurrent A/H3N2 vaccine strains suggesting that these gene segments of H3N2 viruses are evolutionarily more stable compared to H1N1 viruses.
Figures




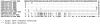

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

