Effect of pre-weaning concentrate supplementation on peripheral distribution of leukocytes, functional activity of neutrophils, acute phase protein and behavioural responses of abruptly weaned and housed beef calves
- PMID: 22217360
- PMCID: PMC3286413
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-1
Effect of pre-weaning concentrate supplementation on peripheral distribution of leukocytes, functional activity of neutrophils, acute phase protein and behavioural responses of abruptly weaned and housed beef calves
Abstract
Background: The effect of pre-weaning concentrate supplementation on peripheral distribution of leukocytes, functional activity of neutrophils, acute phase protein response, metabolic and behavioural response, and performance of abruptly weaned and housed beef calves was investigated. Calves were grazed with their dams until the end of the grazing season when they were weaned and housed (day (d) 0) in a concrete slatted floor shed, and offered grass silage ad libitum plus supplementary concentrates. Twenty-six days prior to weaning and housing, 20 singled suckled, pure-bred Simmental male (non-castrated), (n = 10, m) and female (n = 10, f) calves were assigned to one of two treatments (i) concentrate supplement (CS: n = 10 (5 m and 5 f), mean age (s.d.) 201 (12.8) d, mean weight (s.d.) 258 (20.2) kg) or (ii) no concentrate supplement (controls) (NCS: n = 10, (5 m and 5 f), mean age (s.d.) 201 (13.4) d, mean weight (s.d.) 257 (19.6) kg) pre-weaning.
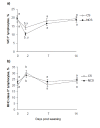
Results: There was a treatment × sampling time interaction (P < 0.05) for percentage CD4+ and WC1+ (γδ T cells) lymphocytes and concentration of plasma globulin. On d 2, percentage CD4+ lymphocytes decreased (P < 0.001) in both treatments. Subsequently on d 7, percentage of CD4+ lymphocytes increased (P < 0.01) in CS compared with d 0, whereas percentage of CD4+ lymphocytes in NCS did not differ (P > 0.05) from d 0. On d 2, WC1+ lymphocytes decreased (P < 0.05) in both treatments but the decrease was greater (P <0.05) in NCS than CS. Subsequently, percentages did not differ (P > 0.05) from pre-weaning baseline. On d 2, the increase in concentration of globulin was greater (P < 0.05) in CS compared with NCS, and subsequently there was no difference between treatments. Pre-weaning ADG was 1.07 (s.e.m.) (0.26) kg and 0.99 (s.e.m.) (0.26) kg for CS and NCS, respectively. Post-weaning, CS calves spent more time lying compared with NCS calves.
Conclusions: Calves supplemented with concentrate prior to weaning had a lesser reduction in WC1+ lymphocytes, increased percentage CD4+ lymphocytes and concentration of total protein, and spent more time lying post-weaning, compared with non-supplemented calves.
© 2012 Lynch et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Martin TG, Lenebager RP, Srinvasan G, Alenda R. Creep feed as a factor influencing performance in cows and calves. J Anim Sci. 1981;53:33–39.
-
- Prichard DL, Hardgrove DD, Olson TA, Marshall TT. Effect of creep feeding, zeranol impacts and breed type on beef productions: 1. Calf and cow performance. J Anim Sci. 1989;67:609–616. - PubMed
-
- Wright IA. The response of spring-born suckled calves to the provision of supplementary feeding when grazing two sward heights in autumn. Anim Prod. 1992;54:197–202. doi: 10.1017/S0003356100036801. - DOI
-
- McGee M, Drennan MJ, Caffrey PJ. Creep concentrates for suckled calves at pasture. Ir J Agric Food Res. 1996;35:71–72.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

