MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation and invasion
- PMID: 22217655
- PMCID: PMC3280801
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor216
MicroRNA-195 plays a tumor-suppressor role in human glioblastoma cells by targeting signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation and invasion
Abstract
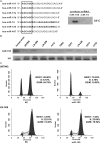
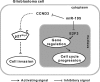
Accumulating evidence has implicated the deregluation of miRNAs in tumorigenesis. Previous studies have reported that microRNA-195 (miR-195) is markedly down-regulated in human glioblastoma cells, compared with normal brain tissue, but the biological role of miR-195 in glioblastoma development is currently unknown. In this study, we define a tumor-suppressor role for miR-195 in human glioblastoma cells. Over-expression of miR-195 in glioblastoma cell lines robustly arrested cell cycle progression and significantly repressed cellular invasion. We identified E2F3 and CCND3 as functional downstream targets of miR-195 in glioblastoma cells. Through knockdown studies, we demonstrated that E2F3 was the dominant effector of miR-195-mediated cell cycle arrest and that CCND3 was a key mediator of miR-195-induced inhibition of glioblastoma cell invasion. Furthermore, we showed that p27(Kip1) was an important regulator downstream of CCND3 and that the accumulation of p27(Kip1) in the cytoplasm might be responsible for the miR-195-mediated cell invasion inhibition in glioblastoma cells. This work provides evidence for the initial mechanism by which miR-195 negatively regulates both the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma cells, suggesting that the down-regulation of miR-195 might contribute to the malignant transformation of glioblastoma cells and could be a molecular signature associated with glioblastoma progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-564 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibited proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma cells by targeting TGF-β1.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 30;7(35):56200-56208. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8987. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27621042 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4.Cancer Lett. 2014 Dec 1;355(1):85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.012. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25218589
-
Up-Regulation of microRNA-183 Promotes Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Glioma By Directly Targeting NEFL.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Nov;36(8):1303-1310. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0328-5. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26879754 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 in targeting glioblastoma stemness.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 10;353(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25042866 Review.
-
Targeting strategies on miRNA-21 and PDCD4 for glioblastoma.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Aug 15;580:64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26142886 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of microRNA expression levels between initial and recurrent glioblastoma specimens.J Neurooncol. 2013 May;112(3):347-54. doi: 10.1007/s11060-013-1078-6. Epub 2013 Feb 19. J Neurooncol. 2013. PMID: 23420397
-
MicroRNA-503 acts as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma for multiple antitumor effects by targeting IGF-1R.Oncol Rep. 2014 Mar;31(3):1445-52. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2951. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24378652 Free PMC article.
-
miR-543 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma in vitro and in vivo.Oncol Rep. 2017 Aug;38(2):725-734. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5712. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28627653 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs and E2F3: a complex network of reciprocal regulations in human cancers.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 21;8(36):60624-60639. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17364. eCollection 2017 Sep 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28947999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional microRNAs in Alzheimer's disease and cancer: differential regulation of common mechanisms and pathways.Front Genet. 2013 Jan 17;3:323. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00323. eCollection 2012. Front Genet. 2013. PMID: 23335942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114(2):97–109. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, et al. Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 2007;21(21):2683–2710. doi:10.1101/gad.1596707. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lefranc F, Brotchi J, Kiss R. Possible future issues in the treatment of glioblastomas: special emphasis on cell migration and the resistance of migrating glioblastoma cells to apoptosis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(10):2411–2422. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.089. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492–507. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0708126. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland EC. Gliomagenesis: genetic alterations and mouse models. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(2):120–129. doi:10.1038/35052535. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

