Skin barrier disruption: a requirement for allergen sensitization?
- PMID: 22217737
- PMCID: PMC3279586
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2011.435
Skin barrier disruption: a requirement for allergen sensitization?
Abstract
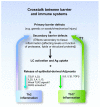
For at least half a century, noninvasive techniques have been available to quantify skin barrier function, and these have shown that a number of human skin conditions and disorders are associated with defects in skin permeability. In the past decade, several genes responsible for skin barrier defects observed in both monogenetic and complex polygenic disorders have been elucidated and functionally characterized. This has led to an explosion of work in the past 6 years that has identified pathways connecting epidermal barrier disruption and antigen uptake, as well as the quality and/or magnitude of the antigen-specific adaptive immune response. This review will introduce the notion that diseases arise from the dynamic crosstalk that occurs between skin barrier and the immune system using atopic dermatitis or eczema as the disease prototype. Nevertheless, the concepts put forth are highly relevant to a number of antigen-driven disorders for which skin barrier is at least transiently compromised, such as psoriasis, allergic contact dermatitis, and blistering disorders.
Figures



References
-
- Akei HS, Brandt EB, Mishra A, et al. Epicutaneous aeroallergen exposure induces systemic TH2 immunity that predisposes to allergic nasal responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118:62–9. - PubMed
-
- Angelova-Fischer I, Fernandez IM, Donnadieu MH, et al. Injury to the stratum corneum induces in vivo expression of human thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:2505–7. - PubMed
-
- Arbesman CE, Wypych JI, Reisman RE, et al. IgE levels in sera of patients with pemphigus or bullous pemphigoid. Archives of dermatology. 1974;110:378–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

