Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulation of the Notch signaling pathway
- PMID: 22218807
- PMCID: PMC3583435
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2012.1620
Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulation of the Notch signaling pathway
Abstract
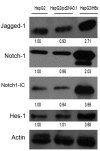
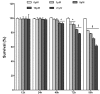
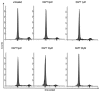
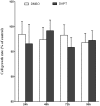
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays a crucial role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), however, little is known about the mechanism. Here, we investigated the relationship between HBx and Notch signaling in HepG2 cells after they were transfected with the HBx gene. It was found that HBx upregulated the expression of Notch-1, Jagged-1 and Hes-1 at the transcriptional level by binding to the Notch-1 intracellular domain, which is congruent with the observations of enhanced malignant biological activities of HBx-transfected HepG2 cells compared with normal HepG2 cells. However, while Notch signaling was blocked, the HBx-induced abnormalities were partially reversed. These findings suggest that HBx may promote the progression of HCC via the activated Notch pathway.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B Virus HBx Activates Notch Signaling via Delta-Like 4/Notch1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 14;11(1):e0146696. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146696. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26766040 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein activates Notch signaling by its effects on Notch1 and Notch4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jan;48(1):329-37. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3221. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26530164
-
Expression of Jagged1 and its association with hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 May 4;356(2):341-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.130. Epub 2007 Mar 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17359939
-
The Jagged-1/Notch-1/Hes-1 pathway is involved in intestinal adaptation in a massive small bowel resection rat model.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Sep;58(9):2478-86. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2680-3. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23595520
-
Role of Notch signaling pathway in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of the literature.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul 21;20(27):9191-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9191. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25083094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel molecular targets in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug 24;11(8):589-605. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i8.589. World J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32879846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Liver Cancer. 2012 Sep;1(2):83-93. doi: 10.1159/000342405. Liver Cancer. 2012. PMID: 24159576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein and TGF-β: partners in the carcinogenic journey of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 19;14:1407434. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1407434. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38962270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Vaproic Acid Induces Cell Growth Arrest in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Suppressing Notch Signaling.J Cancer. 2015 Aug 22;6(10):996-1004. doi: 10.7150/jca.12135. eCollection 2015. J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26366213 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of next-generation sequencing analysis for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma-associated hepatitis B virus mutations.J Biomed Sci. 2018 Jun 2;25(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12929-018-0442-4. J Biomed Sci. 2018. PMID: 29859540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S27–S34. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–1917. - PubMed
-
- Koike K. Hepatitis B virus HBx gene and hepatocarcinogenesis. Intervirology. 1995;38:134–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

