Dexmedetomidine is effective for monitored anesthesia care in outpatients undergoing cataract surgery
- PMID: 22220220
- PMCID: PMC3249565
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.61.6.453
Dexmedetomidine is effective for monitored anesthesia care in outpatients undergoing cataract surgery
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine has a sedative analgesic property without respiratory depression. This study evaluated the efficacy of dexmedetomidine as an appropriate sedative drug for monitored anesthesia care (MAC) in outpatients undergoing cataract surgery on both eyes compared with combination of propofol and alfentanil.
Methods: Thirty-one eligible patients were randomly divided into two groups on the first operation day. Dexmedetomidine was administered in group D at 0.6 µg/kg/h, and propofol and alfentanil was infused concomitantly in group P at a rate of 2 mg/kg/h and 20 µg/kg/h, respectively. Sedation was titrated at Ramsay sedation score 3. Iowa satisfaction with anesthesia scale (ISAS) of the patients was evaluated postoperatively. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), heart rate (HR), respiration rate (RR), and peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO(2)) were recorded throughout the surgery. For the second operation, the group assignments were exchanged.
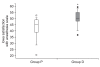
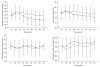
Results: Postoperative ISAS was 50.3 (6.2) in group D and 42.7 (8.7) in group P, which was statistically significant (P < 0.001). SBP was significantly lower in group D compared with group P from the beginning of the operation. HR, RR, and SpO(2) were comparable between the two groups. There were 8 cases (25.8%) of hypertension in group P, and 1 case (3.2%) in group D (P < 0.05). In contrast, 1 case (3.2%) of hypotension and 1 case (3.2%) of bradycardia occurred in group D.
Conclusions: Compared with the combined use of propofol and alfentanil, dexmedetomidine could be used appropriately for MAC in cataract surgery with better satisfaction from the patients and a more stable cardiovascular state.
Keywords: Cataract; Dexmedetomidine; Monitored anesthesia care; Propofol.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Practical Considerations for Dexmedetomidine Sedation in Adult Cataract Surgery Under Local/Regional Anesthesia: A Narrative Review.Anesth Pain Med. 2021 Sep 18;11(4):e118271. doi: 10.5812/aapm.118271. eCollection 2021 Aug. Anesth Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 34692445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for monitored anaesthesia care during cataract surgery.Br J Anaesth. 2006 Jun;96(6):722-6. doi: 10.1093/bja/ael080. Epub 2006 Apr 4. Br J Anaesth. 2006. PMID: 16595611 Clinical Trial.
-
[The application of conscious sedation with a small dose of dexmedetomidine and sufentanil in elderly patients undergoing multiple intestinal polyps resection].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Nov 22;96(43):3474-3478. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.43.007. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27903341 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Dexmedetomidine versus propofol for sedation in patients undergoing vitreoretinal surgery under sub-Tenon's anesthesia.Saudi J Anaesth. 2011 Jan;5(1):36-41. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.76506. Saudi J Anaesth. 2011. PMID: 21655014 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between dexmedetomidine and propofol for sedation in the intensive care unit: patient and clinician perceptions.Br J Anaesth. 2001 Nov;87(5):684-90. doi: 10.1093/bja/87.5.684. Br J Anaesth. 2001. PMID: 11878517 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Sedative, Hemodynamic, and Anesthetic Effect of Dexmedetomidine, Ketamine, and Etomidate on Cataract Surgery by Phacoemulsification Method: A Randomized Clinical Trial.J Curr Ophthalmol. 2023 Apr 29;34(4):414-420. doi: 10.4103/joco.joco_158_22. eCollection 2022 Oct-Dec. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37180533 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Dexmedetomidine Versus Ketamine-Propofol Combination for Sedation in Cataract Surgery.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2015 Apr;43(2):84-90. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2014.45220. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2015. PMID: 27366473 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine: a guide to its use for sedation in the US.Clin Drug Investig. 2012 Aug 1;32(8):561-7. doi: 10.1007/BF03261910. Clin Drug Investig. 2012. PMID: 22741747
-
Intravenous versus perineural dexmedetomidine as adjuvant in adductor canal block for total knee arthroplasty.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023 Aug;76(4):307-316. doi: 10.4097/kja.22579. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 36732321 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Practical Considerations for Dexmedetomidine Sedation in Adult Cataract Surgery Under Local/Regional Anesthesia: A Narrative Review.Anesth Pain Med. 2021 Sep 18;11(4):e118271. doi: 10.5812/aapm.118271. eCollection 2021 Aug. Anesth Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 34692445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosenfeld SI, Litinsky SM, Snyder DA, Plosker H, Astrove AW, Schiffman J. Effectiveness of monitored anesthesia care in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 1999;106:1256–1260. - PubMed
-
- Cok OY, Ertan A, Bahadir M. Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2008;59:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Celiker V, Basgul E, Sahin A, Uzun S, Bahadir B, Aypar U. Comparison of midazolam, propofol and fentanyl combinations for sedation and hemodynamic parameters in cataract extraction. Saudi Med J. 2007;28:1198–1203. - PubMed
-
- Frey K, Sukhani R, Pawlowski J, Pappas AL, Mikat-Stevens M, Slogoff S. Propofol versus propofol-ketamine sedation for retrobulbar nerve block: comparison of sedation quality, intraocular pressure changes, and recovery profiles. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Weinbroum AA, Szold O, Ogorek D, Flaishon R. The midazolam-induced paradox phenomenon is reversible by flumazenil. Epidemiology, patient characteristics and review of the literature. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2001;18:789–797. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

