Non-cell autonomous influence of the astrocyte system xc- on hypoglycaemic neuronal cell death
- PMID: 22220511
- PMCID: PMC3275339
- DOI: 10.1042/AN20110030
Non-cell autonomous influence of the astrocyte system xc- on hypoglycaemic neuronal cell death
Abstract
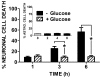
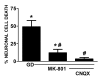
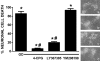
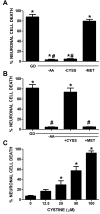
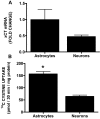
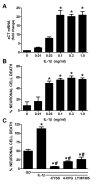
Despite longstanding evidence that hypoglycaemic neuronal injury is mediated by glutamate excitotoxicity, the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved remain incompletely defined. Here, we demonstrate that the excitotoxic neuronal death that follows GD (glucose deprivation) is initiated by glutamate extruded from astrocytes via system xc---an amino acid transporter that imports L-cystine and exports L-glutamate. Specifically, we find that depriving mixed cortical cell cultures of glucose for up to 8 h injures neurons, but not astrocytes. Neuronal death is prevented by ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonism and is partially sensitive to tetanus toxin. Removal of amino acids during the deprivation period prevents--whereas addition of L-cystine restores--GD-induced neuronal death, implicating the cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xc-. Indeed, drugs known to inhibit system xc- ameliorate GD-induced neuronal death. Further, a dramatic reduction in neuronal death is observed in chimaeric cultures consisting of neurons derived from WT (wild-type) mice plated on top of astrocytes derived from sut mice, which harbour a naturally occurring null mutation in the gene (Slc7a11) that encodes the substrate-specific light chain of system xc- (xCT). Finally, enhancement of astrocytic system xc- expression and function via IL-1β (interleukin-1β) exposure potentiates hypoglycaemic neuronal death, the process of which is prevented by removal of l-cystine and/or addition of system xc- inhibitors. Thus, under the conditions of GD, our studies demonstrate that astrocytes, via system xc-, have a direct, non-cell autonomous effect on cortical neuron survival.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Cytotoxic, Co-operative Interaction Between Energy Deprivation and Glutamate Release From System xc- Mediates Aglycemic Neuronal Cell Death.ASN Neuro. 2015 Nov 9;7(6):1759091415614301. doi: 10.1177/1759091415614301. Print 2015 Nov-Dec. ASN Neuro. 2015. PMID: 26553727 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of system x(c)(-)activity and expression in astrocytes by interleukin-1β: implications for hypoxic neuronal injury.Glia. 2010 Nov 15;58(15):1806-15. doi: 10.1002/glia.21050. Glia. 2010. PMID: 20645408 Free PMC article.
-
System x(c)- activity and astrocytes are necessary for interleukin-1 beta-mediated hypoxic neuronal injury.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 19;27(38):10094-105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2459-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17881516 Free PMC article.
-
Glial Glutamate Transporter-Mediated Plasticity: System xc-/xCT/SLC7A11 and EAAT1/2 in Brain Diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 20;28(3):57. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2803057. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37005761 Review.
-
Mechanisms of oxidative glutamate toxicity: the glutamate/cystine antiporter system xc- as a neuroprotective drug target.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Jul;9(3):373-82. doi: 10.2174/187152710791292567. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20053169 Review.
Cited by
-
Mice deficient in L-12/15 lipoxygenase show increased vulnerability to 3-nitropropionic acid neurotoxicity.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Mar 16;643:65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.02.031. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28229935 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis in Acute Central Nervous System Injuries: The Future Direction?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 15;8:594. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00594. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32760721 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β in Central Nervous System Injury and Repair.Eur J Neurodegener Dis. 2012 Aug;1(2):195-211. Eur J Neurodegener Dis. 2012. PMID: 26082912 Free PMC article.
-
Mn Inhibits GSH Synthesis via Downregulation of Neuronal EAAC1 and Astrocytic xCT to Cause Oxidative Damage in the Striatum of Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Aug 30;2018:4235695. doi: 10.1155/2018/4235695. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30228854 Free PMC article.
-
Main path and byways: non-vesicular glutamate release by system xc(-) as an important modifier of glutamatergic neurotransmission.J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(6):1062-79. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13348. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26336934 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Auer RN, Wieloch T, Olsson Y, Siesjo BK. The distribution of hypoglycemic brain damage. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;64:177–191. - PubMed
-
- Backus KH, Kettenmann H, Schachner M. Pharmacological characterization of the glutamate receptor in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 1989;2:274–282. - PubMed
-
- Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW. Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:743–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

