Inflammatory muscle pain is dependent on the activation of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptors and intracellular kinase pathways
- PMID: 22220695
- PMCID: PMC3417434
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01830.x
Inflammatory muscle pain is dependent on the activation of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptors and intracellular kinase pathways
Abstract
Background and purpose: B(1) and B(2) kinin receptors are involved in pain transmission but they may have different roles in the muscle pain induced by intense exercise or inflammation. We investigated the contribution of each of these receptors, and the intracellular pathways involved, in the initial development and maintenance of the muscle pain associated with inflammation-induced tissue damage.
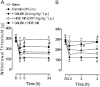
Experimental approach: Mechanical hyperalgesia was measured using the Randall-Selitto apparatus after injecting 5% formalin solution into the gastrocnemius muscle in mice treated with selective antagonists for B(1) or B(2) receptors. The expression of kinin receptors and cytokines and the activation of intracellular kinases were monitored by real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry.
Key results: The i.m. injection of formalin induced an overexpression of B(1) and B(2) receptors. This overexpression was associated with the mechanical hyperalgesia induced by formalin because treatment with B(1) receptor antagonists (des-Arg(9) [Leu(8)]-BK, DALBK, and SSR240612) or B(2) receptor antagonists (HOE 140 and FR173657) prevented the hyperalgesia. Formalin increased myeloperoxidase activity, and up-regulated TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in gastrocnemius. Myeloperoxidase activity and TNF-α mRNA expression were inhibited by either DALBK or HOE 140, whereas IL-6 was inhibited only by HOE 140. The hyperalgesia induced by i.m. formalin was dependent on the activation of intracellular MAPKs p38, JNK and PKC.
Conclusions and implications: Inflammatory muscle pain involves a cascade of events that is dependent on the activation of PKC, p38 and JNK, and the synthesis of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 associated with the up-regulation of both B(1) and B(2) kinin receptors.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
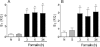

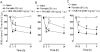




Similar articles
-
Kinin B1 and B2 receptor expression in osteoblasts and fibroblasts is enhanced by interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Effects dependent on activation of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases.Bone. 2008 Jul;43(1):72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.02.003. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18467203
-
The use of kinin B1 and B2 receptor knockout mice and selective antagonists to characterize the nociceptive responses caused by kinins at the spinal level.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Dec;43(7):1188-97. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00311-8. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12504926
-
Anti-nociceptive effect of kinin B₁ and B₂ receptor antagonists on peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;164(2b):681-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01408.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21470206 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK/NF-κB-dependent upregulation of kinin receptors mediates airway hyperreactivity: a new perspective for the treatment.Pharmacol Res. 2013 May;71:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23428345 Review.
-
Kinin B1 receptors: key G-protein-coupled receptors and their role in inflammatory and painful processes.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Dec;143(7):803-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706012. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15520046 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinin Receptors Sensitize TRPV4 Channel and Induce Mechanical Hyperalgesia: Relevance to Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2150-2161. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0475-9. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28283888
-
Preconditioning Contractions Suppress Muscle Pain Markers after Damaging Eccentric Contractions.Pain Res Manag. 2018 Oct 14;2018:3080715. doi: 10.1155/2018/3080715. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 30405861 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV4 Activation and its Intracellular Modulation Mediated by Kinin Receptors Contribute to Painful Symptoms Induced by Anastrozole.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Mar;61(3):1627-1642. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03654-8. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37740866
-
Oxidative Stress Contributes to Fracture/Cast-Induced Inflammation and Pain in a Rat Model of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome.J Pain. 2018 Oct;19(10):1147-1156. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Pain. 2018. PMID: 29715519 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent Bilateral Focal Myositis.Intern Med. 2016;55(22):3369-3374. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.7172. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27853086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angers M, Drouin R, Bachvarova M, Paradis I, Marceau F, Bachvarov DR. In vivo protein-DNA interactions at the kinin B(1) receptor gene promoter: no modification on interleukin-1 beta or lipopolysaccharide induction. J Cell Biochem. 2000;78:278–296. - PubMed
-
- Babenko V, Graven-Nielsen T, Svensson P, Drewes AM, Jensen TS, Arendt-Nielsen L. Experimental human muscle pain and muscular hyperalgesia induced by combinations of serotonin and bradykinin. Pain. 1999;82:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Boix F, Roe C, Rosenborg L, Knardahl S. Kinin peptides in human trapezius muscle during sustained isometric contraction and their relation to pain. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98:534–540. - PubMed
-
- Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982;78:206–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

