Comparison of acute versus convalescent stage high-sensitivity C-Reactive protein level in predicting clinical outcome after acute ischemic stroke and impact of erythropoietin
- PMID: 22222005
- PMCID: PMC3286363
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-6
Comparison of acute versus convalescent stage high-sensitivity C-Reactive protein level in predicting clinical outcome after acute ischemic stroke and impact of erythropoietin
Abstract
Background and aim: Currently, no data on the optimal time point after acute ischemic stroke (IS) at which high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level is most predictive of unfavorable outcome. We tested the hypothesis that hs-CRP levels during both acute (48 h after IS) and convalescent (21 days after IS) phases are equally important in predicting 90-day clinical outcome after acute IS. We further evaluated the impact of erythropoietin (EPO), an anti-inflammatory agent, on level of hs-CRP after acute IS.
Methods: Totally 160 patients were prospectively randomized to receive either EPO therapy (group 1, n = 80) (5,000 IU each time, subcutaneously) at 48 h and 72 h after acute IS, or placebo (group 2, n = 80). Serum level of hs-CRP was determined using ELISA at 48 h and on day 21 after IS and once in 60 healthy volunteers.
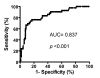
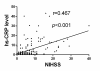
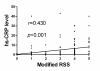
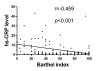
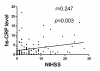
Results: Serum level of hs-CRP was substantially higher in all patients with IS than in healthy controls at 48 h and day 21 after IS (all p < 0.001). Levels of hs-CRP did not differ between group 1 and 2 at 48 h and day 21 after IS (all p > 0.5). Multivariate analysis showed that hs-CRP levels (at 48 h and day 21) were independently predictive of 90-day major adverse neurological event (MANE) (defined as recurrent stroke, NIHSS≥8, or death) (all p < 0.03), whereas EPO therapy was independently predictive of reduced 90-day MANE (all p < 0.02).
Conclusion: EPO therapy which was independently predictive of freedom from 90-day MANE did not alter the crucial role of hs-CRP levels measured at 48 h and 21-day in predicting unfavorable clinical outcome after IS.
Figures
References
-
- van der Wal AC, Becker AE, van der Loos CM, Das PK. Site of intimal rupture or erosion of thrombosed coronary atherosclerotic plaques is characterized by an inflammatory process irrespective of the dominant plaque morphology. Circulation. 1994. pp. 36–44. - PubMed
-
- Yip HK, Sun CK, Chang LT, Wu CJ. Strong correlation between serum levels of inflammatory mediators and their distribution in infarct-related coronary artery. Circ J. 2006. pp. 838–845. - PubMed
-
- Yip HK, Wu CJ, Yang CH, Chang HW, Fang CY, Hung WC, Hang CL. Serial changes in circulating concentrations of soluble cd40 ligand and c-reactive protein in patients with unstable angina undergoing coronary stenting. Circ J. 2005. pp. 890–895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

