Adeno-associated virus-mediated brain delivery of 5-lipoxygenase modulates the AD-like phenotype of APP mice
- PMID: 22222029
- PMCID: PMC3277480
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-7-1
Adeno-associated virus-mediated brain delivery of 5-lipoxygenase modulates the AD-like phenotype of APP mice
Abstract
Background: The 5-lipoxygenase (5LO) enzymatic pathway is widely distributed within the central nervous system. Previous works showed that this protein is up-regulated in Alzheimer's disease (AD), and that its genetic absence results in a reduction of Amyloid beta (Aβ) levels in the Tg2576 mice.Here by employing an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector system to over-express 5LO in the same mouse model, we examined its contribution to their cognitive impairments and brain AD-like amyloid pathology.
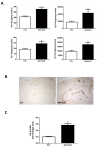
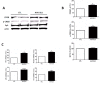
Results: Our results showed that compared with controls, 5LO-targeted gene brain over-expression in Tg2576 mice results in significant memory deficits. On the other hand, brain tissues had a significant elevation in the levels of Aβ peptides and deposition, no change in the steady state levels of amyloid-β precursor protein (APP), BACE-1 or ADAM-10, but a significant increase in PS1, nicastrin, and Pen-2, three major components of the γ-secretase complex. Additional data indicate that the transcription factor CREB was elevated and so were the mRNA levels for PS1, nicastrin and Pen-2.
Conclusions: These data demonstrate that neuronal 5LO plays a functional role in the pathogenesis of AD-like amyloidotic phenotype by modulating the γ-secretase pathway. They support the hypothesis that this enzyme is a novel therapeutic target for the treatment and prevention of AD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
5-Lipoxygenase gene disruption reduces amyloid-beta pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.FASEB J. 2008 Apr;22(4):1169-78. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9131.com. Epub 2007 Nov 12. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 17998412 Free PMC article.
-
Zileuton improves memory deficits, amyloid and tau pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 7;8(8):e70991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070991. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951061 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of 5-lipoxygenase activating protein in the amyloidotic phenotype of an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jun 14;9:127. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-127. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22697885 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-Lipoxygenase as modulator of Alzheimer's γ-secretase and therapeutic target.Brain Res Bull. 2016 Sep;126(Pt 2):207-212. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Brain Res Bull. 2016. PMID: 27005438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel lipid signaling pathways in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 15;88(4):560-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24269629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential contribution of lipoxygenase isozymes to nigrostriatal vulnerability.Neuroscience. 2013 Jan 3;228:73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23079635 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-lipoxygenase pathway: oxidative and inflammatory contributions to the Alzheimer's disease phenotype.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan 14;8:436. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00436. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25642165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of gamma-secretase activating protein by the 5Lipoxygenase: in vitro and in vivo evidence.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 16;5:11086. doi: 10.1038/srep11086. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26076991 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic inhibition of phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α does not block Aβ-dependent elevation of BACE1 and APP levels or reduce amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e101643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101643. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24992504 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: Advancement of Knowledge of Brucella Over the Past 50 Years.Front Vet Sci. 2015 Aug 31;2:27. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2015.00027. eCollection 2015. Front Vet Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664956 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lammers CH, Schweitzer P, Facchinetti P, Arrang JM, Madamba SG, Siggins GR, Piomelli D. Arachidonate 5-lipoxyygenase and its activating protein: prominent hippocampal expression and role in somatostatin signaling. J Neurochem. 1996;66:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Uz T, Pesold C, Longone P, Manev H. Age-associated up-regulation of neuronal 5-lipoxygenase expression: putative role in neuronal vulnerability. FABEB J. 1998;123:439–449. - PubMed

