Determinants of vitamin D status among overweight and obese Puerto Rican adults
- PMID: 22222318
- PMCID: PMC3567879
- DOI: 10.1159/000335282
Determinants of vitamin D status among overweight and obese Puerto Rican adults
Abstract
Background/aims: Low vitamin D status is highly prevalent worldwide, and the major determinants are sun exposure and vitamin D intake. We aimed to measure vitamin D status in a sample of overweight/obese adults in Puerto Rico, an area with plenty of sun exposure, and relate it to vitamin D intake, sun exposure and body composition.
Methods: Serum 25(OH)D levels (liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry), body weight and fat (bioimpedance), vitamin D intake and sun exposure (questionnaires) were assessed. Analysis included age-adjusted correlations and multivariate regression.
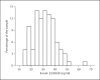
Results: In 98 subjects (66% females; 40-65 years), median serum 25(OH)D levels were 30.7 ng/ml (25-75th percentile 25.0-37.3); 55% had levels >30 ng/ml, 31% had levels between 20 and 30 ng/ml and 14% had levels <20 ng/ml. Total vitamin D intake was 180 IU/day (45-615), and the sun exposure score was 22 (17-27). After adjusting for gender, 25(OH)D levels were significantly correlated with vitamin D intake (r = 0.24, p = 0.018), the sum of sun exposure and vitamin D intake indices (r = 0.34, p = 0.001) and percent body fat (r = -0.25, p = 0.01). After adjusting for age, gender and percent body fat, the sum of sun exposure and vitamin D intake indices remained statistically associated with 25(OH)D levels (β = 1.5, p < 0.01).
Conclusions: In this group of overweight and obese individuals, 25(OH)D was significantly related to vitamin D intake, sun exposure and vitamin D intake indices and percent body fat.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Bandeira F, Griz L, Dreyer P, Eufrazino C, Bandeira C, Freese E. Vitamin D deficiency: a global perspective. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2006;50:640–646. - PubMed
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D: importance in the prevention of cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79:362–371. - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine . Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D. Washington: The National Academy Press; 2011.
-
- Lips P, Hosking D, Lippuner K, Norquist JM, Wehren L, Maalouf G, Ragi-Eis S, Chandler J. The prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy amongst women with osteoporosis: an international epidemiological investigation. J Intern Med. 2006;260:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Nesby-O'Dell S, Scanlon KS, Cogswell ME, Gillespie C, Hollis BW, Looker AC, Allen C, Doughertly C, Gunter EW, Bowman BA. Hypovitaminosis D prevalence and determinants among African American and white women of reproductive age: third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76:187–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical