[¹²⁵I]SD-7015 reveals fine modalities of CB₁ cannabinoid receptor density in the prefrontal cortex during progression of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22222721
- PMCID: PMC4180663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.11.004
[¹²⁵I]SD-7015 reveals fine modalities of CB₁ cannabinoid receptor density in the prefrontal cortex during progression of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
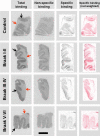
The cannabinoid type-1 receptor (CB₁R) is one of the most abundant members of the G protein-coupled receptor family in the central nervous system. Once activated by their cognate ligands, endocannabinoids, CB₁Rs generally limit the timing of neurotransmitter release at many cortical synapses. Prior studies have indicated the involvement of CB₁R in neurodegeneration and in various neuronal insults, with an emphasis on their neuroprotective role. In the present study we used a novel selective CB₁R radioligand to investigate regional variations in CB₁R ligand binding as a factor of progressive Braak tau pathology in the frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. The frontal cortex was chosen for this study due to the high density of CB₁Rs and their well-characterized involvement in the progression of AD. Post-mortem prefrontal cortex samples from AD patients from Braak stages I to VI and controls were subjected to CB₁R autoradiography with [¹²⁵I]SD-7015 as radioligand. Regional concentration of [¹²⁵I]SD-7015, corresponding to, and thereby representing, regional CB₁R densities, were expressed in fM/g_tissue. The results show that CB₁R density inversely correlates with Braak tau pathology with the following tendency: controls <AD Braak stage V-VI <AD Braak stage III-IV <AD Braak stage I-II. Differences were significant between control and AD Braak stage I-II groups, as well as between controls and the AD group comprising all Braak stages. These findings indicate an up-regulation of the tissue binding of the selective CB₁R radioligand [¹²⁵I]SD7015 in human brains, allowing the detection of fine modalities of receptor expression and radioligand binding during the progression of AD.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
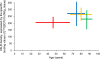
Similar articles
-
Concerted changes in transcripts in the prefrontal cortex precede neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2010 Dec;133(Pt 12):3699-723. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq258. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Brain. 2010. PMID: 20889584
-
Associations between quantitative [18F]flortaucipir tau PET and atrophy across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Jul 4;11(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0510-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31272512 Free PMC article.
-
The decrease of dopamine D₂/D₃ receptor densities in the putamen and nucleus caudatus goes parallel with maintained levels of CB₁ cannabinoid receptors in Parkinson's disease: a preliminary autoradiographic study with the selective dopamine D₂/D₃ antagonist [³H]raclopride and the novel CB₁ inverse agonist [¹²⁵I]SD7015.Brain Res Bull. 2012 Apr 10;87(6):504-10. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.02.012. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Brain Res Bull. 2012. PMID: 22421165 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo SPECT and ex vivo autoradiographic brain imaging of the novel selective CB1 receptor antagonist radioligand [125I]SD7015 in CB1 knock-out and wildtype mouse.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Feb;91:46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23318272 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchical Distribution of the Tau Cytoskeletal Pathology in the Thalamus of Alzheimer's Disease Patients.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;49(4):905-15. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150639. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26519431 Review.
Cited by
-
Anandamide Effects in a Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer's Disease-Like Sporadic Dementia in Rats.Front Neurosci. 2018 Sep 21;12:653. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00653. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30333717 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Therapeutic Targets to Modulate the Endocannabinoid System in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 5;25(7):4050. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074050. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Neurolipid Signaling and Specific Lipid Species in the Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 12;22(22):12256. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212256. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830150 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial Endocannabinoid Signalling in AD.Cells. 2022 Apr 6;11(7):1237. doi: 10.3390/cells11071237. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory Control Deficits Associated with Upregulation of CB1R in the HIV-1 Tat Transgenic Mouse Model of Hand.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;14(4):661-678. doi: 10.1007/s11481-019-09867-w. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31372820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacci A, Huguenard JR, Prince DA. Long-lasting self-inhibition of neocortical interneurons mediated by endocannabinoids. Nature. 2004;431:312–316. - PubMed
-
- Baskin DG, Wimpy H. Calibration of [14C] plastic standards for quantitative autoradiography of [125I] labeled ligands with Amersham Hyperfilm β-max. Neurosci. Lett. 1989;104:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Berrendero F, Romero J, García-Gil L, Suarez I, De la Cruz P, Ramos JA, Fernández-Ruiz JJ. Changes in cannabinoid receptor binding and mRNA levels in several brain regions of aged rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1407:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

