Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons
- PMID: 22222875
- PMCID: PMC3727154
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3133
Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons
Abstract
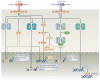
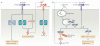
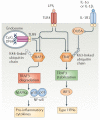
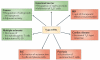
Interferon-α (IFNα) and IFNβ, collectively known as type I IFNs, are the major effector cytokines of the host immune response against viral infections. However, the production of type I IFNs is also induced in response to bacterial ligands of innate immune receptors and/or bacterial infections, indicating a broader physiological role for these cytokines in host defence and homeostasis than was originally assumed. The main focus of this Review is the underappreciated immunomodulatory functions of type I IFNs in health and disease. We discuss their function in the regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses, the response to bacterial ligands, inflammasome activation, intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Salaman RN. Protective inoculation against a plant virus. Nature. 1933;131:468.
-
- White PB. Lysogenic strains of V. cholerae and the influence of lysozyme on cholera phage activity. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1937;44:276–278.
-
- Hoskins M. A protective action of neurotropic against viscerotropic yellow fever virus in Macacus rhesus. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1935;15:675–680.
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1957;147:258–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

