Beyond lung function in COPD management: effectiveness of LABA/LAMA combination therapy on patient-centred outcomes
- PMID: 22222945
- PMCID: PMC6547888
- DOI: 10.4104/pcrj.2011.00102
Beyond lung function in COPD management: effectiveness of LABA/LAMA combination therapy on patient-centred outcomes
Abstract
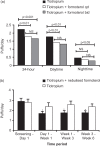
Bronchodilators are central to the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Clinical studies combining different classes of bronchodilators, in particular a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) and a long-acting β2-agonist (LABA), have demonstrated greater improvements in lung function (forced expiratory volume in 1 second, FEV1) in patients with COPD than monotherapy. FEV1 has served as an important diagnostic measurement of COPD, and the majority of clinical studies of currently available pharmacotherapies grade effectiveness of treatment regimens based on improvements in FEV1. However, FEV1 alone may not adequately reflect the overall health status of the patient. Published evidence suggests that LABA/LAMA combination therapies demonstrate greater improvements in patient-centred outcomes such as dyspnoea, symptoms, rescue medication use, and quality of life than individual drugs used alone. Evaluating patient-centred outcomes associated with COPD is likely to play an important role in future research as a measure of overall treatment effectiveness. Raising awareness of the importance of outcomes beyond lung function alone, particularly in primary care where most patients initially present themselves for medical evaluation, should form a fundamental part of a more holistic approach to COPD management.
Conflict of interest statement
TvdM has received research grants from AstraZeneca (AZ), GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Nycomed, and MSD; consultancy fees from AZ, Nycomed, MSD, and Novartis; and speaker fees from AZ, GSK, Nycomed and MSD. MC has received honoraria for speaking and consulting and/or financial support for attending meetings from Abbott, AZ, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi Farmaceutici, Dey, Gentili, GSK, Lallemand, Menarini Farmaceutici, Mundipharma, Novartis, Nycomed, Pfizer, Sanovel, Sigma Tau, and Valeas.
Figures
References
-
- GOLD. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2009.
-
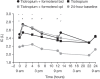
- van Noord JA, Aumann JL, Janssens E, et al. Effects of tiotropium with and without formoterol on airflow obstruction and resting hyperinflation in patients with COPD. Chest 2006;129(3):509–17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.129.3.509 - PubMed
-
- Cazzola M, Matera MG. Long-acting bronchodilators are the first-choice option for the treatment of stable COPD. Chest 2004;125(1):9–11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.125.1.9 - PubMed
-
- Hanania NA, Donohue JF. Pharmacologic interventions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: bronchodilators. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2007;4(7):526–34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1513/pats.200701-016FM - PubMed
-
- Cazzola M, Molimard M. The scientific rationale for combining long-acting beta2-agonists and muscarinic antagonists in COPD. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 2010;23(4):257–67. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pupt.2010.03.003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
