Trojan horse strategies used by pathogens to influence the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) system of host eukaryotic cells
- PMID: 22223032
- PMCID: PMC3696380
- DOI: 10.1159/000335027
Trojan horse strategies used by pathogens to influence the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) system of host eukaryotic cells
Abstract
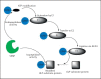
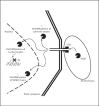
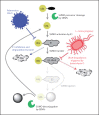
A remarkable feature of pathogenic organisms is their ability to utilize the cellular machinery of host cells to their advantage in facilitating their survival and propagation. Posttranslational modification of proteins offers a quick way to achieve changes in the localization, binding partners or functions of a target protein. It is no surprise then that pathogens have evolved multiple ways to interfere with host posttranslational modifications and hijack them for their own purposes. Recently, modification of proteins by small ubiquitin-like modifier has emerged as an important posttranslational modification regulating transcription, DNA repair and cell division, and literature has started to emerge documenting how it could be utilized by pathogenic bacteria and viruses during infection. In this brief review, we focus on the host small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) system and how disease causing agents influence SUMO conjugation and deconjugation, highlighting the common theme of global hypoSUMOylation upon infection by pathogens.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M. Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:159–180. - PubMed
-
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell. 1995;80:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Ruddock LW, Molinari M. N-glycan processing in ER quality control. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:4373–4380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

