Killing cells by targeting mitosis
- PMID: 22223105
- PMCID: PMC3278741
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.197
Killing cells by targeting mitosis
Abstract
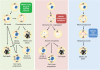
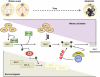
Cell cycle deregulation is a common feature of human cancer. Tumor cells accumulate mutations that result in unscheduled proliferation, genomic instability and chromosomal instability. Several therapeutic strategies have been proposed for targeting the cell division cycle in cancer. Whereas inhibiting the initial phases of the cell cycle is likely to generate viable quiescent cells, targeting mitosis offers several possibilities for killing cancer cells. Microtubule poisons have proved efficacy in the clinic against a broad range of malignancies, and novel targeted strategies are now evaluating the inhibition of critical activities, such as cyclin-dependent kinase 1, Aurora or Polo kinases or spindle kinesins. Abrogation of the mitotic checkpoint or targeting the energetic or proteotoxic stress of aneuploid or chromosomally instable cells may also provide further benefits by inducing lethal levels of instability. Although cancer cells may display different responses to these treatments, recent data suggest that targeting mitotic exit by inhibiting the anaphase-promoting complex generates metaphase cells that invariably die in mitosis. As the efficacy of cell-cycle targeting approaches has been limited so far, further understanding of the molecular pathways modulating mitotic cell death will be required to move forward these new proposals to the clinic.
Figures

References
-
- Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Mammalian cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:630–641. - PubMed
-
- Malumbres M, Barbacid M. To cycle or not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:222–231. - PubMed
-
- Malumbres M, Pevarello P, Barbacid M, Bischoff JR. CDK inhibitors in cancer therapy: what is next. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2008;29:16–21. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro GI. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1770–1783. - PubMed
-
- Rane SG, Dubus P, Mettus RV, Galbreath EJ, Boden G, Reddy EP, et al. Loss of Cdk4 expression causes insulin-deficient diabetes and Cdk4 activation results in beta-islet cell hyperplasia. Nat Genet. 1999;22:44–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

