Left-right symmetry breaking in tissue morphogenesis via cytoskeletal mechanics
- PMID: 22223355
- PMCID: PMC3288887
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.255927
Left-right symmetry breaking in tissue morphogenesis via cytoskeletal mechanics
Abstract
Rationale: Left-right (LR) asymmetry is ubiquitous in animal development. Cytoskeletal chirality was recently reported to specify LR asymmetry in embryogenesis, suggesting that LR asymmetry in tissue morphogenesis is coordinated by single- or multi-cell organizers. Thus, to organize LR asymmetry at multiscale levels of morphogenesis, cells with chirality must also be present in adequate numbers. However, observation of LR asymmetry is rarely reported in cultured cells.
Objectives: Using cultured vascular mesenchymal cells, we tested whether LR asymmetry occurs at the single cell level and in self-organized multicellular structures.
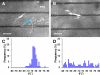
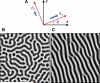
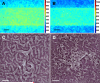
Methods and results: Using micropatterning, immunofluorescence revealed that adult vascular cells polarized rightward and accumulated stress fibers at an unbiased mechanical interface between adhesive and nonadhesive substrates. Green fluorescent protein transfection revealed that the cells each turned rightward at the interface, aligning into a coherent orientation at 20° relative to the interface axis at confluence. During the subsequent aggregation stage, time-lapse videomicroscopy showed that cells migrated along the same 20° angle into neighboring aggregates, resulting in a macroscale structure with LR asymmetry as parallel, diagonal stripes evenly spaced throughout the culture. Removal of substrate interface by shadow mask-plating, or inhibition of Rho kinase or nonmuscle myosin attenuated stress fiber accumulation and abrogated LR asymmetry of both single-cell polarity and multicellular coherence, suggesting that the interface triggers asymmetry via cytoskeletal mechanics. Examination of other cell types suggests that LR asymmetry is cell-type specific.
Conclusions: Our results show that adult stem cells retain inherent LR asymmetry that elicits de novo macroscale tissue morphogenesis, indicating that mechanical induction is required for cellular LR specification.
Figures





References
-
- Okumura T, Utsuno H, Kuroda J, Gittenberger E, Asami T, Matsuno K. The Development and Evolution of Left-Right Asymmetry in Invertebrates: Lessons From Drosophila and Snails. Dev Dyn. 2008;237:3497–3515. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M, Shinohara K, Wang J, Ikeuchi S, Yoshiba S, Meno C, Nonaka S, Takada S, Hatta K, Wynshaw-Boris A, Hamada H. Planar polarization of node cells determines the rotational axis of node cilia. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Danilchik MV, Brown EE, Riegert K. Intrinsic chiral properties of the Xenopus egg cortex: an early indicator of left-right asymmetry? Development. 2006;133:4517–4526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

