Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin/sulbactam in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing extended dialysis
- PMID: 22223613
- PMCID: PMC3302675
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05690611
Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin/sulbactam in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing extended dialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: The fixed antibacterial combination of ampicillin and sulbactam is frequently used for various infections. Intact kidneys eliminate approximately 71% of ampicillin and 78% of sulbactam. Patients on thrice-weekly low-flux hemodialysis exhibit an ampicillin t(1/2) of 2.3 hours on and 17.4 hours off dialysis. Despite its frequent use in intensive care units, there are no available dosing recommendations for patients with AKI undergoing renal replacement therapy. The aims of this study were to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of ampicillin/sulbactam in critically ill patients with AKI undergoing extended dialysis (ED) and to establish a dosing recommendation for this treatment method.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Twelve critically ill patients with anuric AKI being treated with ED were enrolled in a prospective, open-label, observational pharmacokinetic study. Pharmacokinetics after a single dose of ampicillin/sulbactam (2 g/1 g) was obtained in 12 patients. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics after 4 days of twice-daily ampicillin/sulbactam (2 g/1 g) was obtained in three patients.
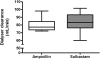
Results: The mean dialyzer clearance for ampicillin/sulbactam was 80.1 ± 7.7/83.3 ± 12.1 ml/min. The t(1/2) of ampicillin and sulbactam in patients with AKI undergoing ED were 2.8 ± 0.8 hours and 3.5 ± 1.5 hours, respectively. There was no significant accumulation using a twice-daily dosage of 2 g/1 g ampicillin/sulbactam.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that in patients treated with ED using a high-flux dialyzer (polysulphone, 1.3 m(2); blood and dialysate flow, 160 ml/min; treatment time, 480 minutes), a twice-daily dosing schedule of at least 2 g/1 g ampicillin/sulbactam, with one dose given after ED, should be used to avoid underdosing.
Figures
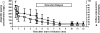
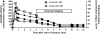
Comment in
-
Adding to the armamentarium: antibiotic dosing in extended dialysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Mar;7(3):373-5. doi: 10.2215/CJN.00650112. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22344505 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lode HM: Rational antibiotic therapy and the position of ampicillin/sulbactam. Int J Antimicrob Agents 32: 10–28, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Polk RE, Fox C, Mahoney A, Letcavage J, MacDougall C: Measurement of adult antibacterial drug use in 130 US hospitals: Comparison of defined daily dose and days of therapy. Clin Infect Dis 44: 664–670, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Fliser D, Kielstein JT: Technology insight: Treatment of renal failure in the intensive care unit with extended dialysis. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2: 32–39, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kumar VA, Yeun JY, Depner TA, Don BR: Extended daily dialysis vs. continuous hemodialysis for ICU patients with acute renal failure: A two-year single center report. Int J Artif Organs 27: 371–379, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

