Structural insights into apoptotic DNA degradation by CED-3 protease suppressor-6 (CPS-6) from Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 22223640
- PMCID: PMC3293555
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.316075
Structural insights into apoptotic DNA degradation by CED-3 protease suppressor-6 (CPS-6) from Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
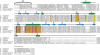
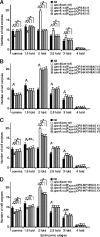
Endonuclease G (EndoG) is a mitochondrial protein that traverses to the nucleus and participates in chromosomal DNA degradation during apoptosis in yeast, worms, flies, and mammals. However, it remains unclear how EndoG binds and digests DNA. Here we show that the Caenorhabditis elegans CPS-6, a homolog of EndoG, is a homodimeric Mg(2+)-dependent nuclease, binding preferentially to G-tract DNA in the optimum low salt buffer at pH 7. The crystal structure of CPS-6 was determined at 1.8 Å resolution, revealing a mixed αβ topology with the two ββα-metal finger nuclease motifs located distantly at the two sides of the dimeric enzyme. A structural model of the CPS-6-DNA complex suggested a positively charged DNA-binding groove near the Mg(2+)-bound active site. Mutations of four aromatic and basic residues: Phe(122), Arg(146), Arg(156), and Phe(166), in the protein-DNA interface significantly reduced the DNA binding and cleavage activity of CPS-6, confirming that these residues are critical for CPS-6-DNA interactions. In vivo transformation rescue experiments further showed that the reduced DNase activity of CPS-6 mutants was positively correlated with its diminished cell killing activity in C. elegans. Taken together, these biochemical, structural, mutagenesis, and in vivo data reveal a molecular basis of how CPS-6 binds and hydrolyzes DNA to promote cell death.
Figures



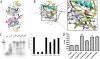
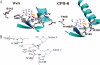

References
-
- Cummings O. W., King T. C., Holden J. A., Low R. L. (1987) Purification and characterization of the potent endonuclease in extracts of bovine heart mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 2005–2015 - PubMed
-
- Low R. L. (2003) Mitochondrial endonuclease G function in apoptosis and mtDNA metabolism. A historical perspective. Mitochondrion 2, 225–236 - PubMed
-
- Parrish J., Li L., Klotz K., Ledwich D., Wang X., Xue D. (2001) Mitochondrial endonuclease G is important for apoptosis in C. elegans. Nature 412, 90–94 - PubMed
-
- Li L. Y., Luo X., Wang X. (2001) Endonuclease G is an apoptotic DNase when released from mitochondria. Nature 412, 95–99 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

