Safety and prolonged activity of recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein in hemophilia A patients
- PMID: 22223821
- PMCID: PMC3646317
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-382846
Safety and prolonged activity of recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein in hemophilia A patients
Abstract
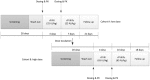
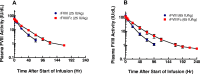
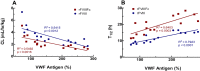
Current factor VIII (FVIII) products display a half-life (t(1/2)) of ∼ 8-12 hours, requiring frequent intravenous injections for prophylaxis and treatment of patients with hemophilia A. rFVIIIFc is a recombinant fusion protein composed of a single molecule of FVIII covalently linked to the Fc domain of human IgG(1) to extend circulating rFVIII t(1/2). This first-in-human study in previously treated subjects with severe hemophilia A investigated safety and pharmacokinetics of rFVIIIFc. Sixteen subjects received a single dose of rFVIII at 25 or 65 IU/kg followed by an equal dose of rFVIIIFc. Most adverse events were unrelated to study drug. None of the study subjects developed anti-rFVIIIFc antibodies or inhibitors. Across dose levels, compared with rFVIII, rFVIIIFc showed 1.54- to 1.70-fold longer elimination t(1/2), 1.49- to 1.56-fold lower clearance, and 1.48- to 1.56-fold higher total systemic exposure. rFVIII and rFVIIIFc had comparable dose-dependent peak plasma concentrations and recoveries. Time to 1% FVIII activity above baseline was ∼ 1.53- to 1.68-fold longer than rFVIII across dose levels. Each subject showed prolonged exposure to rFVIIIFc relative to rFVIII. Thus, rFVIIIFc may offer a viable therapeutic approach to achieve prolonged hemostatic protection and less frequent dosing in patients with hemophilia A. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01027377.
Figures
Comment in
-
Longer FVIII: the 4th generation.Blood. 2012 Mar 29;119(13):2972-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-403675. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22461469
Similar articles
-
Recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein: extended-interval dosing maintains low bleeding rates and correlates with von Willebrand factor levels.J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Nov;12(11):1788-800. doi: 10.1111/jth.12723. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25196897 Clinical Trial.
-
Recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein for the prevention and treatment of bleeding in children with severe hemophilia A.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Jun;13(6):967-77. doi: 10.1111/jth.12911. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25912075 Clinical Trial.
-
Population pharmacokinetics of recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein.Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2015 May-Jun;4(3):163-74. doi: 10.1002/cpdd.167. Epub 2014 Oct 27. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2015. PMID: 27140796 Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy of Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein: A Practical Review.J Infus Nurs. 2017 Jan/Feb;40(1):65-75. doi: 10.1097/NAN.0000000000000205. J Infus Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28030484 Review.
-
Efmoroctocog Alfa: A Review in Haemophilia A.Drugs. 2021 Nov;81(17):2035-2046. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01615-w. Epub 2021 Nov 7. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34743314 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting Individual Changes in Terminal Half-Life After Switching to Extended Half-Life Concentrates in Patients With Severe Hemophilia.Hemasphere. 2022 Mar 21;6(4):e694. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000694. eCollection 2022 Apr. Hemasphere. 2022. PMID: 35356797 Free PMC article.
-
A novel B-domain O-glycoPEGylated FVIII (N8-GP) demonstrates full efficacy and prolonged effect in hemophilic mice models.Blood. 2013 Mar 14;121(11):2108-16. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-407494. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23335368 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immune responses by the neonatal fc receptor and its therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 5;5:664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00664. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25601863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A French Real-World Evidence Study Evaluating the Efficacy, Safety, and Pharmacokinetic Parameters of rVIII-SingleChain in Patients with Hemophilia A Receiving Prophylaxis.Thromb Haemost. 2023 May;123(5):490-500. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1761449. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Thromb Haemost. 2023. PMID: 36758611 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Hemophilia A Using Factor VIII Messenger RNA Lipid Nanoparticles.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Jun 5;20:534-544. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.03.015. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32330871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mannucci PM, Tuddenham EGD. The haemophiliac: from royal genes to gene therapy. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(23):1773–1779. - PubMed
-
- Soucie JM, Nuss R, Evatt B, et al. Mortality among males with hemophilia: relationship with source of medical care. The Hemophilia Surveillance System Project Investigators. Blood. 2000;96(2):437–442. - PubMed
-
- Manco-Johnson M, Abshire TC, Shapiro A, et al. Prophylaxis versus episodic treatment to prevent joint disease in boys with severe hemophilia. New Engl J Med. 2007;357(6):535–544. - PubMed
-
- Aledort L, Haschmeyer R, Pettersson H. A longitudinal study of orthopaedic outcomes for severe factor-VIII-deficient haemophiliacs. The Orthopaedic Outcome Study Group. J Intern Med. 1994;236(4):391–399. - PubMed
-
- Petrini P, Lindvall N, Egberg N, Blomback M. Prophylaxis with factor concentrates in preventing hemophilic arthropathy. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1991;13(3):280–287. - PubMed

