Randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of wrap therapy for wound healing acceleration in patients with NPUAP stage II and III pressure ulcer
- PMID: 22223842
- PMCID: PMC3253421
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000371
Randomised controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of wrap therapy for wound healing acceleration in patients with NPUAP stage II and III pressure ulcer
Abstract
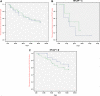
Objectives To evaluate if 'wrap therapy' using food wraps, which is widely used in Japanese clinical sites, is not inferior when compared to guideline adhesion treatments. Design Multicentre, prospective, randomised, open, blinded endpoint clinical trial. Setting 15 hospitals in Japan. Patients 66 older patients with new National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel stage II or III pressure ulcers. Interventions Of these 66 patients, 31 were divided into the conventional treatment guidelines group and 35 into the wrap therapy group. Main outcome measures The primary end point was the period until the pressure ulcers were cured. The secondary end point was a comparison of the speed of change in the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing score. Results 64 of the 66 patients were analysed. The estimated mean period until healing was 57.5 days (95% CI 45.2 to 69.8) in the control group as opposed to 59.8 days (95% CI 49.7 to 69.9) in the wrap therapy group. By the extent of pressure ulcer infiltration, the mean period until healing was 16.0 days (95% CI 8.1 to 23.9) in the control group as opposed to 18.8 days (95% CI 10.3 to 27.2) in the wrap therapy group with National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel stage II ulcers, and 71.8 days (95% CI 61.4 to 82.3) as opposed to 63.2 days (95% CI 53.0 to 73.4), respectively, with stage III ulcers. There is no statistical significance in difference in Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing scores. Conclusions It might be possible to consider wrap therapy as an alternative choice in primary care settings as a simple and inexpensive dressing care. Clinical Trial registration UMIN Clinical Trials Registry UMIN000002658. Summary protocol is available on https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-bin/ctr/ctr.cgi?function=brows&action=brows&type=detail&recptno=R000003235&admin=0&language=J.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Brem H, Lyder C. Protocol for the successful treatment of pressure ulcers. Am J Surg 2004;188(1A Suppl):9–17 - PubMed
-
- Orlando PL. Pressure ulcer management in the geriatric patient. Ann Pharmacother 1998;32:1221–7 - PubMed
-
- Smith DM. Pressure ulcers in the nursing home. Ann Intern Med 1995;123:433–42 - PubMed
-
- Agency for Health Care Policy and Research Pressure ulcer treatment: Clinical Practice Guideline Quick Reference Guide. 1994;15:1–25 - PubMed
-
- Cullum N, Nelson EA, Flemming K, et al. Systematic reviews of wound care management: (5) beds; (6) compression; (7) laser therapy, therapeutic ultrasound, electrotherapy and electromagnetic therapy. Health Technol Assess 2001;5:1–221 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
