Unusual binding of ursodeoxycholic acid to ileal bile acid binding protein: role in activation of FXRα
- PMID: 22223860
- PMCID: PMC3307643
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M021733
Unusual binding of ursodeoxycholic acid to ileal bile acid binding protein: role in activation of FXRα
Abstract
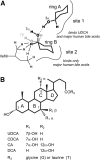
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, ursodiol) is used to prevent damage to the liver in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. The drug also prevents the progression of colorectal cancer and the recurrence of high-grade colonic dysplasia. However, the molecular mechanism by which UDCA elicits its beneficial effects is not entirely understood. The aim of this study was to determine whether ileal bile acid binding protein (IBABP) has a role in mediating the effects of UDCA. We find that UDCA binds to a single site on IBABP and increases the affinity for major human bile acids at a second binding site. As UDCA occupies one of the bile acid binding sites on IBABP, it reduces the cooperative binding that is often observed for the major human bile acids. Furthermore, IBABP is necessary for the full activation of farnesoid X receptor α (FXRα) by bile acids, including UDCA. These observations suggest that IBABP may have a role in mediating some of the intestinal effects of UDCA.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of ileal bile acid-binding protein expression in Caco-2 cells by ursodeoxycholic acid: role of the farnesoid X receptor.Biochem Pharmacol. 2005 Jun 15;69(12):1755-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.03.019. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15935148
-
Comparative potency of obeticholic acid and natural bile acids on FXR in hepatic and intestinal in vitro cell models.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017 Dec;5(6):e00368. doi: 10.1002/prp2.368. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017. PMID: 29226620 Free PMC article.
-
A novel variant of ileal bile acid binding protein is up-regulated through nuclear factor-kappaB activation in colorectal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Res. 2007 Oct 1;67(19):9039-46. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3690. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17909007
-
Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid on cholesterol and bile acid metabolism.Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):1007-18. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90708-0. Gastroenterology. 1986. PMID: 3527851 Review.
-
Primary Biliary Cholangitis: Medical and Specialty Pharmacy Management Update.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Oct;22(10-a-s Suppl):S3-S15. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.10-a-s.s3. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27700211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ostα-/- mice exhibit altered expression of intestinal lipid absorption genes, resistance to age-related weight gain, and modestly improved insulin sensitivity.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;306(5):G425-38. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00368.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24381083 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoproteomic Profiling of Bile Acid Interacting Proteins.ACS Cent Sci. 2017 May 24;3(5):501-509. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00134. Epub 2017 May 5. ACS Cent Sci. 2017. PMID: 28573213 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary (iso)BAs cooperate with endogenous ligands to activate FXR under physiological and pathological conditions.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Aug 1;1867(8):166153. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166153. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33895309 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Absorption of Bile Acids in Health and Disease.Compr Physiol. 2019 Dec 18;10(1):21-56. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c190007. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31853951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of cytoplasmic lipid droplets in each region of the small intestine of lean and diet-induced obese mice in response to dietary fat.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):G75-G86. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00084.2021. Epub 2021 May 19. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34009042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beuers U. 2006. Drug insight: mechanisms and sites of action of ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestasis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3: 318–328 - PubMed
-
- LaRusso N. F., Shneider B. L., Black D., Gores G. J., James S. P., Doo E., Hoofnagle J. H. 2006. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 44: 746–764 - PubMed
-
- Tung B. Y., Emond M. J., Haggitt R. C., Bronner M. P., Kimmey M. B., Kowdley K. V., Brentnall T. A. 2001. Ursodiol use is associated with lower prevalence of colonic neoplasia in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 134: 89–95 - PubMed
-
- Pardi D. S., Loftus E. V. J., Kremers W. K., Keach J., Lindor K. D. 2003. Ursodeoxycholic acid as a chemopreventive agent in patients with ulcerative colitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gastroenterology. 124: 889–893 - PubMed
-
- Alberts D. S., Martinez M. E., Hess L. M., Einspahr J. G., Green S. B., Bhattacharyya A. K., Guillen J., Krutzsch M., Batta A. K., Salen G., et al. 2005. Phase III trial of ursodeoxycholic acid to prevent colorectal adenoma recurrence. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 97: 846–853 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

