Factor VIII light chain contains a binding site for factor X that contributes to the catalytic efficiency of factor Xase
- PMID: 22224589
- PMCID: PMC3298758
- DOI: 10.1021/bi201731p
Factor VIII light chain contains a binding site for factor X that contributes to the catalytic efficiency of factor Xase
Abstract
Factor (F) VIII functions as a cofactor in FXase, markedly accelerating the rate of FIXa-catalyzed activation of FX. Earlier work identified a FX-binding site having μM affinity within the COOH-terminal region of the FVIIIa A1 subunit. In the present study, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), ELISA-based binding assays, and chemical cross-linking were employed to assess an interaction between FX and the FVIII light chain (A3C1C2 domains). SPR and ELISA-based assays showed that FVIII LC bound to immobilized FX (K(d) = 165 and 370 nM, respectively). Furthermore, active site-modified activated protein C (DEGR-APC) effectively competed with FX in binding FVIII LC (apparent K(i) = 82.7 nM). Western blotting revealed that the APC-catalyzed cleavage rate at Arg(336) was inhibited by FX in a concentration-dependent manner. A synthetic peptide comprising FVIII residues 2007-2016 representing a portion of an APC-binding site blocked the interaction of FX and FVIII LC (apparent K(i) = 152 μM) and directly bound to FX (K(d) = 7.7 μM) as judged by SPR and chemical cross-linking. Ala-scanning mutagenesis of this sequence revealed that the A3C1C2 subunit derived from FVIII variants Thr2012Ala and Phe2014Ala showed 1.5- and 1.8-fold increases in K(d) for FX, whereas this value using the A3C1C2 subunit from a Thr2012Ala/Leu2013Ala/Phe2014Ala triple mutant was increased >4-fold. FXase formed using this LC triple mutant demonstrated an ~4-fold increase in the K(m) for FX. These results identify a relatively high affinity and functional FX site within the FVIIIa A3C1C2 subunit and show a contribution of residues Thr2012 and Phe2014 to this interaction.
Figures
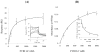
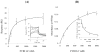




Similar articles
-
Contribution of factor VIII light-chain residues 2007-2016 to an activated protein C-interactive site.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Feb;109(2):187-98. doi: 10.1160/TH12-08-0561. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23224054 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Factor VIII A2 Domain Residues 400-409 to a Factor X-Interactive Site in the Factor Xase Complex.Thromb Haemost. 2018 May;118(5):830-841. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1637745. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29614522
-
Model for the factor VIIIa-dependent decay of the intrinsic factor Xase. Role of subunit dissociation and factor IXa-catalyzed proteolysis.J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 15;271(11):6027-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.11.6027. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8626386
-
Role of activation of the coagulation factor VIII in interaction with vWf, phospholipid, and functioning within the factor Xase complex.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Oct;9(7):185-92. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(00)00019-0. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999. PMID: 10881749 Review.
-
The protein structure and effect of factor VIII.Thromb Res. 2007;119(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2005.12.015. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Thromb Res. 2007. PMID: 16487577 Review.
Cited by
-
Factor VIIIa-mimetic cofactor activity of a bispecific antibody to factors IX/IXa and X/Xa, emicizumab, depends on its ability to bridge the antigens.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jun 28;117(7):1348-1357. doi: 10.1160/TH17-01-0030. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 28451690 Free PMC article.
-
A Molecular Revolution in the Treatment of Hemophilia.Mol Ther. 2020 Apr 8;28(4):997-1015. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.11.006. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31843450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of emicizumab on global coagulation assays for plasma supplemented with apixaban or argatroban.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Apr;49(3):413-419. doi: 10.1007/s11239-019-01993-9. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 31728842
-
Emicizumab, a humanized bispecific antibody to coagulation factors IXa and X with a factor VIIIa-cofactor activity.Int J Hematol. 2020 Jan;111(1):20-30. doi: 10.1007/s12185-018-2545-9. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Int J Hematol. 2020. PMID: 30350119 Review.
-
Contribution of factor VIII light-chain residues 2007-2016 to an activated protein C-interactive site.Thromb Haemost. 2013 Feb;109(2):187-98. doi: 10.1160/TH12-08-0561. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Thromb Haemost. 2013. PMID: 23224054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mann KG, Nesheim ME, Church WR, Haley P, Krishnaswamy S. Surface-dependent reactions of the vitamin K-dependent enzyme complexes. Blood. 1990;76:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Miyahara N, Shoda J, Ishige K, Kawamoto T, Ueda T, Taki R, Ohkohchi N, Hyodo I, Thomas MB, Krishnamurthy S, Carraway KL, Irimura T. MUC4 interacts with ErbB2 in human gallbladder carcinoma: potential pathobiological implications. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:1048–1056. - PubMed
-
- Vehar GA, Keyt B, Eaton D, Rodriguez H, O’Brien DP, Rotblat F, Oppermann H, Keck R, Wood WI, Harkins RN, et al. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984;312:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Fay PJ, Anderson MT, Chavin SI, Marder VJ. The size of human factor VIII heterodimers and the effects produced by thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;871:268–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

