Reflex principles of immunological homeostasis
- PMID: 22224768
- PMCID: PMC4533843
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075015
Reflex principles of immunological homeostasis
Abstract
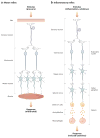
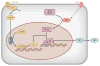
The reasoning that neural reflexes maintain homeostasis in other body organs, and that the immune system is innervated, prompted a search for neural circuits that regulate innate and adaptive immunity. This elucidated the inflammatory reflex, a prototypical reflex circuit that maintains immunological homeostasis. Molecular products of infection or injury activate sensory neurons traveling to the brainstem in the vagus nerve. The arrival of these incoming signals generates action potentials that travel from the brainstem to the spleen and other organs. This culminates in T cell release of acetylcholine, which interacts with α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α7 nAChR) on immunocompetent cells to inhibit cytokine release in macrophages. Herein is reviewed the neurophysiological basis of reflexes that provide stability to the immune system, the neural- and receptor-dependent mechanisms, and the potential opportunities for developing novel therapeutic devices and drugs that target neural pathways to treat inflammatory diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:871–82. - PubMed
-
- Loewi O. Über homorale Übertragbarkeit der Herznervenwirkung. Pflügers Archiv. 1921;189:239–42.
-
- Sherrington C. The Integrative Action of the Nervous System. New Haven, CT: Yale Univ. Press; 1906.
-
- Tracey KJ. The inflammatory reflex. Nature. 2002;420:853–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

