Presynaptic inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis by kappa opioid receptor signaling
- PMID: 22225848
- PMCID: PMC3314138
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.11.015
Presynaptic inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis by kappa opioid receptor signaling
Abstract
Background: The kappa opioid receptor (KOR) and its endogenous agonist, the neuropeptide dynorphin, are a critical component of the central stress system. Both dynorphin and KOR are expressed in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), a brain region associated with anxiety and stress. This suggests that KOR activation in this region may play a role in the regulation of emotional behaviors. To date, however, there has been no investigation of the ability of KOR to modulate synaptic transmission in the BNST.
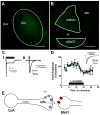
Methods: We used whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from acutely prepared mouse brain slices to examine the actions of KOR on inhibitory transmission in the BNST. Additionally, we used neurochemical and pathway-specific optogenetic manipulations to selectively stimulate gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic fibers from the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) to the BNST.
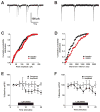
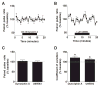
Results: We found that activation of KOR reduced GABAergic transmission through a presynaptic mechanism. Furthermore, we examined the signal transduction pathways that mediate this inhibition and provide the first functional information implicating extracellular signal-regulated kinase in KOR-mediated presynaptic modulation. Moreover, we found that at KOR signaling robustly reduced inhibitory synaptic transmission in the CeA to BNST pathway.
Conclusions: Together, these results demonstrate that KOR provides important inhibitory control over presynaptic GABAergic signaling within the BNST and provides the first direct functional demonstration of KOR-sensitive long-range GABAergic connections between the CeA and the BNST.
Copyright © 2012 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest to report.
Figures




References
-
- Madaan V, Wilson DR. Neuropeptides: relevance in treatment of depression and anxiety disorders. Drug News Perspect. 2009;22:319–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AA019454/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA017668/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK057521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK089044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK057521/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA019454/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R00AA017668/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK046200/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK075632/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

