TAK1 negatively regulates NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase activation in Gr-1+CD11b+ neutrophils
- PMID: 22226633
- PMCID: PMC3750978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.12.010
TAK1 negatively regulates NF-κB and p38 MAP kinase activation in Gr-1+CD11b+ neutrophils
Erratum in
- Immunity. 2012 Jan 27;36(1):153
Abstract
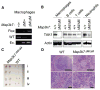
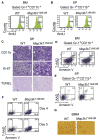
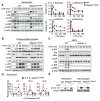
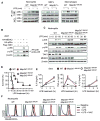
Stringent control of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling is critical during innate immune responses. TGF-β activated kinase-1 (TAK1) is essential for NF-κB activation in T and B cells but has precisely the opposite activity in myeloid cells. Specific deletion of TAK1 (Map3k7(ΔM/ΔM)) led to development of splenomegaly and lymphomegaly associated with neutrophilia. Compared with wild-type cells, TAK1-deficient neutrophils enhanced the phosphorylation of the kinases IKK, p38, and JNK and the production of interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. Map3k7(ΔM/ΔM) mice were significantly more susceptible to LPS-induced septic shock and produced higher amounts of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in plasma than do wild-type mice. Specific ablation of p38 rescued the phenotype and functional properties of Map3k7(ΔM/ΔM) mice. Our findings identify a previously unrecognized role of TAK1 as a negative regulator of p38 and IKK activation in a cell type-specific manner.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Adhikari A, Xu M, Chen ZJ. Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene. 2007;26:3214–3226. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Asehnoune K, Strassheim D, Mitra S, Kim JY, Abraham E. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 2004;172:2522–2529. - PubMed
-
- Bettermann K, Vucur M, Haybaeck J, Koppe C, Janssen J, Heymann F, Weber A, Weiskirchen R, Liedtke C, Gassler N, et al. TAK1 suppresses a NEMO-dependent but NF-kappaB-independent pathway to liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:481–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

