Role of the adenosine(2A) receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
- PMID: 22227265
- PMCID: PMC3348415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2011.12.002
Role of the adenosine(2A) receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension
Abstract
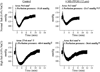
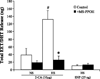
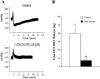
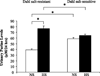
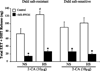
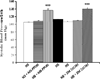
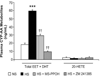
Activation of rat adenosine(2A) receptors (A(2A) R) dilates preglomerular microvessels, an effect mediated by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). High salt (HS) intake increases epoxygenase activity and adenosine levels. A greater vasodilator response to a stable adenosine analog, 2-chloroadenosine (2-CA), was seen in kidneys obtained from HS-fed rats which was mediated by increased EET release. Because this pathway is antipressor, we examined the role of the A(2A) R-EET pathway in a genetic model of salt-sensitive hypertension, the Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rats. Dahl salt resistant (SR) rats fed a HS diet demonstrated a greater renal vasodilator response to 2-CA. In contrast, Dahl SS rats did not exhibit a difference in the vasodilator response to 2-CA whether fed normal salt (NS) or HS diet. In Dahl SR but not Dahl SS rats, HS intake significantly increased purine flux, augmented the protein expression of A(2A) R and cytochrome P450 2C23 and 2C11 epoxygenases, and elevated the renal efflux of EETs. Thus the Dahl SR rat is able to respond to HS intake by recruiting EET formation, whereas the Dahl SS rat appears to have exhausted its ability to increase EET synthesis above the levels observed on NS intake. In vivo inhibition of the A(2A) R-EET pathway in Dahl SR rats fed a HS diet results in reduced renal EETs levels, diminished natriuretic capacity and hypertension, thus supporting a role for the A(2A) R-EET pathway in the adaptive natriuretic response to modulate blood pressure during salt loading. An inability of Dahl SS rats to upregulate the A(2A) R-EET pathway in response to salt loading may contribute to the development of salt-sensitive hypertension.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase in regulating renal membrane transport and hypertension.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013 Mar;22(2):163-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835d911e. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23302865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Failure to upregulate the adenosine2A receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway contributes to the development of hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Dec;295(6):F1696-704. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90502.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18829737 Free PMC article.
-
Purinoceptors in renal microvessels: adenosine-activated and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase-derived arachidonate metabolites.Pharmacol Rep. 2005;57 Suppl:191-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2005. PMID: 16415499 Review.
-
Inhibition of the adenosine2A receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway renders Dahl salt-resistant rats hypertensive.Hypertension. 2009 Dec;54(6):1284-90. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.123570. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19822802 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated response to adenosine in kidneys from high salt-fed rats: role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):F386-92. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00421.2004. Epub 2005 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15814528
Cited by
-
Role of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase in regulating renal membrane transport and hypertension.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013 Mar;22(2):163-9. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32835d911e. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23302865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinoceptor: a novel target for hypertension.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09852-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35181831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Adenosine A1 and A2a Receptors in Cerebral Blood Vessel Reactivity of Sprague Dawley Rats Exposed to Hyperbaric Oxygenation.Molecules. 2025 Jul 10;30(14):2918. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142918. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733187 Free PMC article.
-
A synthetic epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analogue prevents the initiation of ischemic acute kidney injury.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019 Oct;227(2):e13297. doi: 10.1111/apha.13297. Epub 2019 Jun 2. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 31077555 Free PMC article.
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): A novel class of second messengers of hormonal functional responses.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2025 Mar;177:106967. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2025.106967. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2025. PMID: 39889333 Review.
References
-
- He FJ, Jenner KH, Macgregor GA. WASH-world action on salt and health. Kidney Int. 2010;78(8):745–753. - PubMed
-
- Cowley AW., Jr Genetic and nongenetic determinants of salt sensitivity and blood pressure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65(2 Suppl):587S–593S. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Purinergic receptors in the heart. Circ Res. 1980;46(6 Pt 2):I175–I182. - PubMed
-
- Olah ME, Stiles GL. The role of receptor structure in determining adenosine receptor activity. Pharmacol Ther. 2000;85(2):55–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

