Core lab analysis of baseline echocardiographic studies in the STICH trial and recommendation for use of echocardiography in future clinical trials
- PMID: 22227341
- PMCID: PMC3310914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2011.12.002
Core lab analysis of baseline echocardiographic studies in the STICH trial and recommendation for use of echocardiography in future clinical trials
Abstract
Background: The Surgical Treatment for Ischemic Heart Failure (STICH) randomized trial was designed to identify an optimal management strategy for patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Baseline echocardiographic examinations were required for all patients. The primary aim of this report is to describe the baseline STICH Echocardiography Core Laboratory data. The secondary aim is to provide recommendations regarding how echocardiography should be used in clinical practice and research on the basis of the experience gained from echocardiography in STICH.
Methods: Between September 2002 and January 2006, 2,136 patients with ejection fractions (EFs) ≤ 35% and coronary artery disease amenable to coronary artery bypass grafting were enrolled. Echocardiography was acquired by 122 clinical enrolling sites, and measurements were performed by the Echocardiography Core Laboratory after a certification process for all clinical sites.
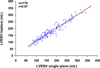
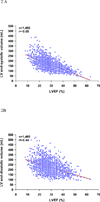
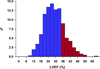
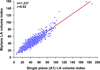
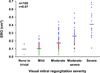
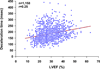
Results: Echocardiography was available for analysis in 2,006 patients (93.9%); 1,734 (86.4%) were men, and the mean age was 60.9 ± 9.5 years. The mean left ventricular end-systolic volume index, measureable in 72.8%, was 84.0 ± 30.9 mL/m(2), and the mean EF was 28.9 ± 8.3%, with 18.5% of patients having EFs > 35%. Single-plane measurements of left ventricular and left atrial volumes were similar to their volumes by biplane measurement (r = 0.97 and r = 0.92, respectively). Mitral regurgitation severity by visual assessment was associated with a wide range of effective regurgitant orifice area, while effective regurgitant orifice area ≥ 0.2 cm(2) indicated at least moderate mitral regurgitation by visual assessment. Deceleration time of mitral inflow velocity had a weak correlation with EF (r = 0.25) but was inversely related to estimated pulmonary artery systolic pressure (r = -0.49).
Conclusions: In STICH patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy, Echocardiography Core Laboratory analysis of baseline echocardiographic findings demonstrated a wide spectrum of left ventricular shape, function, and hemodynamics, as well as the feasibility and limitations of obtaining essential echocardiographic measurements. It is critical that the use of echocardiographic parameters in clinical practice and research balance the strengths and weaknesses of the technique.
Copyright © 2012 American Society of Echocardiography. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gaining respect for echocardiographic volumetric quantitation: observations on a study of the baseline echocardiography data from the STICH echocardiography core laboratory.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012 Mar;25(3):337-40. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2012.01.020. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2012. PMID: 22353338 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lang R, Bierig M, Devereux R, Flachskampf F, Foster E, Pellikka P, et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a Branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:1440–1463. - PubMed
-
- Enriquez-Sarano M, Seward J, Bailey K, Tajik A. Effective regurgitant orifice area: a noninvasive Doppler development of an old hemodynamic concept. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;23:443–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

