Matrix metalloproteinase-dependent microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 expression in macrophages: role of TNF-α and the EP4 prostanoid receptor
- PMID: 22227567
- PMCID: PMC3273587
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102383
Matrix metalloproteinase-dependent microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 expression in macrophages: role of TNF-α and the EP4 prostanoid receptor
Erratum in
-
Correction: Matrix Metalloproteinase-Dependent Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase-1 Expression in Macrophages: Role of TNF-α and the EP4 Prostanoid Receptor.J Immunol. 2021 Jul 15;207(2):746-747. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100445. Epub 2021 Jul 2. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34215658 No abstract available.
Abstract
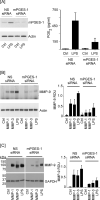
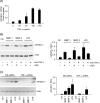
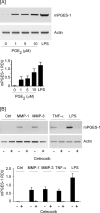
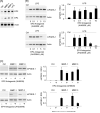
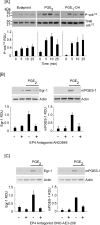
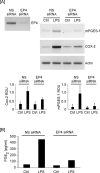
Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 contributes to the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Thus, identifying targetable components of signaling pathways that regulate MMP-9 expression may have broad therapeutic implications. Our previous studies revealed a nexus between metalloproteinases and prostanoids whereby MMP-1 and MMP-3, commonly found in inflammatory and neoplastic foci, stimulate macrophage MMP-9 expression via the release of TNF-α and subsequent induction of cyclooxygenase-2 and PGE(2) engagement of EP4 receptor. In the current study, we determined whether MMP-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression was coupled to the expression of prostaglandin E synthase family members. We found that MMP-1- and MMP-3-dependent release of TNF-α induced rapid and transient expression of early growth response protein 1 in macrophages followed by sustained elevation in microsomal prostaglandin synthase 1 (mPGES-1) expression. Metalloproteinase-induced PGE(2) levels and MMP-9 expression were markedly attenuated in macrophages in which mPGES-1 was silenced, thereby identifying mPGES-1 as a therapeutic target in the regulation of MMP-9 expression. Finally, the induction of mPGES-1 was regulated, in part, through a positive feedback loop dependent on PGE(2) binding to EP4. Thus, in addition to inhibiting macrophage MMP-9 expression, EP4 antagonists emerge as potential therapy to reduce mPGES-1 expression and PGE(2) levels in inflammatory and neoplastic settings.
Figures

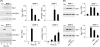


References
-
- Nagase H, Okada Y. Proteinases and Matrix Degradation. In: Kelly WN, Harris ED Jr., Ruddy S, Sledge CB, editors. The Textbook of Rheumatology. 5 ed. W.B.Saunders; Philadelphia: 1996. pp. 323–341.
-
- Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Van Damme J. Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends in Immunology. 2001;22:571–579. - PubMed
-
- Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2004;4:617–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

