CHCM1/CHCHD6, novel mitochondrial protein linked to regulation of mitofilin and mitochondrial cristae morphology
- PMID: 22228767
- PMCID: PMC3293568
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.277103
CHCM1/CHCHD6, novel mitochondrial protein linked to regulation of mitofilin and mitochondrial cristae morphology
Abstract
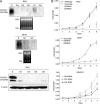
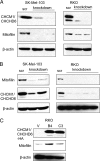
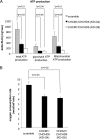
The structural integrity of mitochondrial cristae is crucial for mitochondrial functions; however, the molecular events controlling the structural integrity and biogenesis of mitochondrial cristae remain to be fully elucidated. Here, we report the functional characterization of a novel mitochondrial protein named CHCM1 (coiled coil helix cristae morphology 1)/CHCHD6. CHCM1/CHCHD6 harbors a coiled coil helix-coiled coil helix domain at its C-terminal end and predominantly localizes to mitochondrial inner membrane. CHCM1/CHCHD6 knockdown causes severe defects in mitochondrial cristae morphology. The mitochondrial cristae in CHCM1/CHCHD6-deficient cells become hollow with loss of structural definitions and reduction in electron-dense matrix. CHCM1/CHCHD6 depletion also leads to reductions in cell growth, ATP production, and oxygen consumption. CHCM1/CHCHD6 through its C-terminal end strongly and directly interacts with the mitochondrial inner membrane protein mitofilin, which is known to also control mitochondrial cristae morphology. CHCM1/CHCHD6 also interacts with other mitofilin-associated proteins, including DISC1 and CHCHD3. Knockdown of CHCM1/CHCHD6 reduces mitofilin protein levels; conversely, mitofilin knockdown leads to reduction in CHCM1 levels, suggesting coordinate regulation between these proteins. Our results further indicate that genotoxic anticancer drugs that induce DNA damage down-regulate CHCM1/CHCHD6 expression in multiple human cancer cells, whereas mitochondrial respiratory chain inhibitors do not affect CHCM1/CHCHD6 levels. CHCM1/CHCHD6 knockdown in human cancer cells enhances chemosensitivity to genotoxic anticancer drugs, whereas its overexpression increases resistance. Collectively, our results indicate that CHCM1/CHCHD6 is linked to regulation of mitochondrial cristae morphology, cell growth, ATP production, and oxygen consumption and highlight its potential as a possible target for cancer therapeutics.
Figures








References
-
- Czarnecka A. M., Marino Gammazza A., Di Felice V., Zummo G., Cappello F. (2007) Cancer as a “Mitochondriopathy.” J. Cancer Mol. 3, 71–79
-
- Kirkinezos I. G., Moraes C. T. (2001) Reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 449–457 - PubMed
-
- Toyokuni S., Okamoto K., Yodoi J., Hiai H. (1995) Persistent oxidative stress in cancer. FEBS Lett. 358, 1–3 - PubMed
-
- Warburg O. (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123, 309–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

