Semecarpus anacardium Linn.: A review
- PMID: 22228947
- PMCID: PMC3249908
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-7847.65328
Semecarpus anacardium Linn.: A review
Abstract
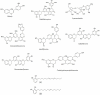
Semecarpus anacardium Linn. (Family: Anacardiaceae), commonly known 'Ballataka' or 'Bhilwa', has been used in various traditional system of medicines for various ailments since ancient times. Its nuts contain a variety of biologically active compounds such as biflavonoids, phenolic compounds, bhilawanols, minerals, vitamins and amino acids, which show various medicinal properties. The fruit and nut extract shows various activities like antiatherogenic, antiinflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-reproductive, CNS stimulant, hypoglycemic, anticarcinogenic and hair growth promoter. The article reviews the various activities of the plant.
Keywords: Antiinflammatory; Semecarpus anacardium; bhilawanols; hypoglycemic; nut extract.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Farnsworth NR, Soejarto DD. Global importance of medicinal plants. In: Akerele O, Heywood V, Synge H, editors. Conserv Med Plants. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1991. pp. 25–51.
-
- Dhalla S, Chan KJ, Montaner JS, Hogg RS. Complementary and alternative medicine use in British Columbia: A survey of HIV positive people on antiretroviral therapy. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2006;12:242–8. - PubMed
-
- Chopra RN. 2nd ed. Calcutta: Academic Publishers; 1982. Indigenous drugs of India; pp. 407–9.
-
- Khare CP. Encyclopedia of Indian medicinal plants. Encyclopedia of Indian Medicinal Plants. 1982:419–21.
-
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. Vol. 3. Dehradun, India: International Booksellers and Publishers; 1975. Indian medicinal plants; p. 667.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources