Free energy, value, and attractors
- PMID: 22229042
- PMCID: PMC3249597
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/937860
Free energy, value, and attractors
Abstract
It has been suggested recently that action and perception can be understood as minimising the free energy of sensory samples. This ensures that agents sample the environment to maximise the evidence for their model of the world, such that exchanges with the environment are predictable and adaptive. However, the free energy account does not invoke reward or cost-functions from reinforcement-learning and optimal control theory. We therefore ask whether reward is necessary to explain adaptive behaviour. The free energy formulation uses ideas from statistical physics to explain action in terms of minimising sensory surprise. Conversely, reinforcement-learning has its roots in behaviourism and engineering and assumes that agents optimise a policy to maximise future reward. This paper tries to connect the two formulations and concludes that optimal policies correspond to empirical priors on the trajectories of hidden environmental states, which compel agents to seek out the (valuable) states they expect to encounter.
Figures
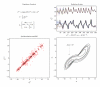
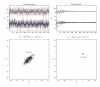
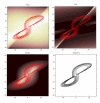
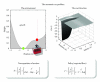
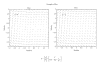
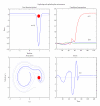
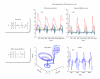
References
-
- Friston K, Kilner J, Harrison L. A free energy principle for the brain. Journal of Physiology Paris. 2006;100(1–3):70–87. - PubMed
-
- Sutton RS, Barto AG. Toward a modern theory of adaptive networks: Expectation and prediction. Psychological Review. 1981;88(2):135–170. - PubMed
-
- Daw ND, Doya K. The computational neurobiology of learning and reward. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2006;16(2):199–204. - PubMed
-
- Dayan P, Daw ND. Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain. Cognitive, Affective and Behavioral Neuroscience. 2008;8(4):429–453. - PubMed
-
- Niv Y, Schoenbaum G. Dialogues on prediction errors. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2008;12(7):265–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

