Prenatal diagnosis of unilateral pulmonary dysplasia
- PMID: 22229061
- PMCID: PMC3252884
Prenatal diagnosis of unilateral pulmonary dysplasia
Abstract
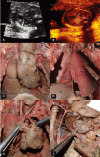
Pulmonary hypoplasia is a rare congenital disorder; most cases occur in association with other congenital abnormalities, including congenital diaphragmatic hernia, oligohydramnios, and/or skeletal deformities. The authors report a case of unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia diagnosed prenatally and confirmed at autopsy.
Keywords: Fetal lung development; Prenatal diagnosis; Pulmonary hypoplasia; Pulmonary vasculature.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: ultrasonic measurement of fetal lungs to predict pulmonary hypoplasia.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Sep;14(3):162-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1999.14030162.x. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10550874
-
A Case of Fatal Pulmonary Hypoplasia with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia, Thoracic Myelomeningocele, and Thoracic Dysplasia.AJP Rep. 2017 Oct;7(4):e234-e237. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1615791. Epub 2017 Dec 29. AJP Rep. 2017. PMID: 29302380 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting neonatal deaths and pulmonary hypoplasia in isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia using the sonographic fetal lung volume-body weight ratio.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008 May;190(5):1216-9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.3078. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. PMID: 18430834
-
Ultrasound prediction of fetal pulmonary hypoplasia in pregnancies complicated by oligohydramnios and in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a review.Am J Perinatol. 1994 Mar;11(2):104-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-994566. Am J Perinatol. 1994. PMID: 8198648 Review.
-
Prenatal prediction of pulmonary hypoplasia.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017 Aug;22(4):245-249. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017. PMID: 28325581 Review.
References
-
- Chen S, Ursell PC, Adatia I, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of primary pulmonary hypoplasia in fraternal twins. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2010;35:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Odd DE, Battin MR, Hallam L, Knight DB. Primary pulmonary hypoplasia: a case report and review of the literature. J Paediatr Child Health. 2003;39:467–469. - PubMed
-
- Vettraino IM, Tawil A, Comstock CH. Bilateral pulmonary agenesis: prenatal sonographic appearance simulates diaphragmatic hernia. J Ultrasound Med. 2003;22:723–726. - PubMed
-
- Kalache KD, Chaoui R, Paris S, Bollmann R. Prenatal diagnosis of right lung agenesis using color Doppler and magnetic resonance imaging. Fetal Diagn Ther. 1997;12:360–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
