Th17 response and inflammatory autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 22229105
- PMCID: PMC3249891
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/819467
Th17 response and inflammatory autoimmune diseases
Abstract
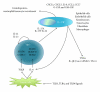
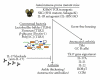
The proinflammatory activity of T helper 17 (Th17) cells can be beneficial to the host during infection. However, uncontrolled or inappropriate Th17 activation has been linked to several autoimmune and autoinflammatory pathologies. Indeed, preclinical and clinical data show that Th17 cells are associated with several autoimmune diseases such as arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, and lupus. Furthermore, targeting the interleukin-17 (IL-17) pathway has attenuated disease severity in preclinical models of autoimmune diseases. Interestingly, a recent report brings to light a potential role for Th17 cells in the autoinflammatory disorder adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD). Whether Th17 cells are the cause or are directly involved in AOSD remains to be shown. In this paper, we discuss the biology of Th17 cells, their role in autoimmune disease development, and in AOSD in particular, as well as the growing interest of the pharmaceutical industry in their use as therapeutic targets.
Figures
References
-
- Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nature Immunology. 2005;6(11):1123–1132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources