Effect of the Japanese herbal medicine, Boiogito, on the osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion
- PMID: 22230247
- PMCID: PMC3275496
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2555-4-3
Effect of the Japanese herbal medicine, Boiogito, on the osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion
Abstract
Background: Boiogito (Japanese herbal medicine, Tsumura Co. Tokyo, Japan) contains sinomenin which inhibits inflammatory reactions. Since sinomenine is a principle component of the Boiogito, there is a possibility of it being effective on osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee with joint effusion. However, there is no report concerning the effectiveness of Boiogito on knee OA. The objective of the present study is to investigate the therapeutic effect of Boiogito on OA of the knee associated with joint effusion in a comparative study among randomly assigned groups.
Methods: Study was performed using 50 patients who were diagnosed with primary osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion. The patients were randomly assigned to two groups: one group (25 patients) using both loxoprofen (2-{4-[(2-oxocyclopentyl) methyl]} propanoic acid) and Boiogito and the other group (25 patients) using loxoprofen, and were evaluated during a 12 week observation period. The assessment parameters including knee scores in the Knee Society Rating System including Knee score and Functional scores, amount of joint effusion by joint puncture in clinically detected cases, the 36-items short form of the Medical Outcome Study Questionnaire (SF-36) as a measurement of health related quality of life were used.
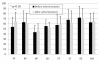
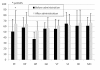
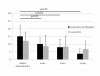
Results: The knee scores based on the Knee Society Rating System were improved in both groups. The staircase climbing up and down ability in the Knee society rating system functional score was significantly improved in the group using Boiogito and loxoprofen compared to the loxoprofen group. In the evaluation using SF-36, significant improvements were found in the scores in both groups in physical functioning after 12 weeks. The amount of joint fluid was significantly decreased at 4, 8 and 12 weeks compared to pre-administration baseline in the group using Boiogito and loxoprofen. A side effect of Boiogito, dry mouth, was found in one case. The symptom was mild and improved immediately after discontinuation of administration.
Conclusion: The results indicated that Boiogito have a possibility for a treatment modality for joint effusion with osteoarthritis of the knee.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden N, Bierma-Zeinstra S, Brandt KD, Croft P, Doherty M, Dougados M, Hochberg M, Hunter DJ, Kwoh K, Lohmander LS, Tugwell P. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part I: Critical appraisal of existing treatment guidelines and systematic review of current research evidence. OsteoArthritis and Cartilage. 2007;15:981–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.06.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pelletier JP, Yaron M, Haraoui B, Cohen P, Nahir MA, Choquette D, Wigler I, Rosner IA, Beaulieu AD. Efficacy and safety of diacerein in osteoarthritis of the knee: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(10):2339–48. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200010)43:10<2339::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dougados M, Nguyen M, Berdah L, Mazieres B, Vignon E, Lequesne M. Evaluation of the structure-modifying effects of diacerein in hip osteoarthritis: ECHODIAH, a three-year, placebo-controlled trial Evaluation of the Chondromodulating Effect of Diacerein in OA of the Hip. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(11):2539–47. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2539::AID-ART434>3.0.CO;2-T. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

