Telomestatin impairs glioma stem cell survival and growth through the disruption of telomeric G-quadruplex and inhibition of the proto-oncogene, c-Myb
- PMID: 22230766
- PMCID: PMC3896097
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1795
Telomestatin impairs glioma stem cell survival and growth through the disruption of telomeric G-quadruplex and inhibition of the proto-oncogene, c-Myb
Abstract
Purpose: Glioma stem cells (GSC) are a critical therapeutic target of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
Experimental design: The effects of a G-quadruplex ligand, telomestatin, were evaluated using patient-derived GSCs, non-stem tumor cells (non-GSC), and normal fetal neural precursors in vitro and in vivo. The molecular targets of telomestatin were determined by immunofluorescence in situ hybridization (iFISH) and cDNA microarray. The data were then validated by in vitro and in vivo functional assays, as well as by immunohistochemistry against 90 clinical samples.
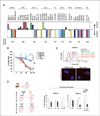
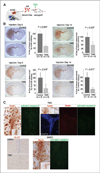
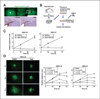
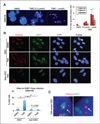
Results: Telomestatin impaired the maintenance of GSC stem cell state by inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. The migration potential of GSCs was also impaired by telomestatin treatment. In contrast, both normal neural precursors and non-GSCs were relatively resistant to telomestatin. Treatment of GSC-derived mouse intracranial tumors reduced tumor sizes in vivo without a noticeable cell death in normal brains. iFISH revealed both telomeric and non-telomeric DNA damage by telomestatin in GSCs but not in non-GSCs. cDNA microarray identified a proto-oncogene, c-Myb, as a novel molecular target of telomestatin in GSCs, and pharmacodynamic analysis in telomestatin-treated tumor-bearing mouse brains showed a reduction of c-Myb in tumors in vivo. Knockdown of c-Myb phenocopied telomestatin-treated GSCs both in vitro and in vivo, and restoring c-Myb by overexpression partially rescued the phenotype. Finally, c-Myb expression was markedly elevated in surgical specimens of GBMs compared with normal tissues.
Conclusions: These data indicate that telomestatin potently eradicates GSCs through telomere disruption and c-Myb inhibition, and this study suggests a novel GSC-directed therapeutic strategy for GBMs.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have seen and approved the manuscript. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting glioma stem cells in vivo by a G-quadruplex-stabilizing synthetic macrocyclic hexaoxazole.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 15;7(1):3605. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03785-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28620243 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex ligand-induced DNA damage response coupled with telomere dysfunction and replication stress in glioma stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Feb 26;471(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.176. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26845351 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of glioma stem-like cells with a parthenolide derivative ACT001 through inhibition of AEBP1/PI3K/AKT signaling.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(2):555-566. doi: 10.7150/thno.49250. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391492 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide disrupts glioma stem cells via promoting PML degradation to inhibit tumor growth.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 10;6(35):37300-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5836. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26510911 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 radiosensitizes glioblastoma xenograft in vivo through a differential targeting of bulky differentiated- and stem-cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 16;38(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1293-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31311580 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
On-Chip Clonal Analysis of Glioma-Stem-Cell Motility and Therapy Resistance.Nano Lett. 2016 Sep 14;16(9):5326-32. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00902. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Nano Lett. 2016. PMID: 27420544 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrosoluble Perylene Monoimide-Based Telomerase Inhibitors with Diminished Cytotoxicity.ACS Omega. 2022 May 5;7(19):16746-16756. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01343. eCollection 2022 May 17. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35601338 Free PMC article.
-
PARP3 is a promoter of chromosomal rearrangements and limits G4 DNA.Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 27;8:15110. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15110. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28447610 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplexes as potential therapeutic targets for embryonal tumors.Molecules. 2013 Oct 10;18(10):12500-37. doi: 10.3390/molecules181012500. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24152672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomere biology and translational research.Transl Res. 2013 Dec;162(6):333-42. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 24070997 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Vescovi AL, Galli R, Reynolds BA. Brain tumour stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:425–436. - PubMed
-
- Kim MY, Vankayalapati H, Shin-Ya K, Wierzba K, Hurley LH. Telomestatin, a potent telomerase inhibitor that interacts quite specifically with the human telomeric intramolecular g-quadruplex. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:2098–2099. - PubMed
-
- d'Adda di Fagagna F, Reaper PM, Clay-Farrace L, Fiegler H, Carr P, Von Zglinicki T, et al. A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence. Nature. 2003;426:194–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

