The effectiveness of chemical denture cleansers and ultrasonic device in biofilm removal from complete dentures
- PMID: 22231005
- PMCID: PMC3973472
- DOI: 10.1590/s1678-77572011000600021
The effectiveness of chemical denture cleansers and ultrasonic device in biofilm removal from complete dentures
Abstract
Adequate denture hygiene can prevent and treat infection in edentulous patients. They are usually elderly and have difficulty for brushing their teeth.
Objective: This study evaluated the efficacy of complete denture biofilm removal using chemical (alkaline peroxide-effervescent tablets), mechanical (ultrasonic) and combined (association of the effervescent and ultrasonic) methods.
Material and methods: Eighty complete denture wearers participated in the experiment for 21 days. They were distributed into 4 groups (n=20): (1) Brushing with water (Control); (2) Effervescent tablets (Corega Tabs); (3) Ultrasonic device (Ultrasonic Cleaner, model 2840 D); (4) Association of effervescent tablets and ultrasonic device. All groups brushed their dentures with a specific brush (Bitufo) and water, 3 times a day, before applying their treatments. Denture biofilm was collected at baseline and after 21 days. To quantify the biofilm, the internal surfaces of the maxillary complete dentures were stained and photographed at 45º. The photographs were processed and the areas (total internal surface stained with biofilm) quantified (Image Tool 2.02). The percentage of the biofilm was calculated by the ratio between the biofilm area multiplied by 100 and the total area of the internal surface of the maxillary complete denture.
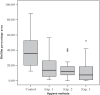
Results: The Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparison among groups followed by the Dunn multiple-comparison test. All tests were performed respecting a significance level of 0.05. Significant difference was found among the treatments (KW=21.18; P<0.001), the mean ranks for the treatments and results for Dunn multiple comparison test were: Control (60.9); Chemical (37.2); Mechanical (35.2) and Combined (29.1).
Conclusion: The experimental methods were equally effective regarding the ability to remove biofilm and were superior to the control method (brushing with water). Immersion in alkaline peroxide and ultrasonic vibration can be used as auxiliary agents for cleaning complete dentures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effervescent tablets and ultrasonic devices against Candida and mutans streptococci in denture biofilm.Gerodontology. 2011 Dec;28(4):264-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-2358.2010.00378.x. Epub 2010 May 26. Gerodontology. 2011. PMID: 20518813 Clinical Trial.
-
Complete denture biofilm after brushing with specific denture paste, neutral soap and artificial saliva.Braz Dent J. 2013;24(1):47-52. doi: 10.1590/0103-6440201301946. Braz Dent J. 2013. PMID: 23657413 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical and antimicrobial efficacy of NitrAdine ™-based disinfecting cleaning tablets in complete denture wearers.J Appl Oral Sci. 2010 Dec;18(6):560-5. doi: 10.1590/s1678-77572010000600005. J Appl Oral Sci. 2010. PMID: 21308285 Free PMC article.
-
Scientific evidence on the efficacy of effervescent tablets for cleaning removable prostheses. A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Prosthet Dent. 2024 Jun;131(6):1071-1083. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2023.01.031. Epub 2023 Mar 2. J Prosthet Dent. 2024. PMID: 36870893
-
Denture hygiene: a review and update.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2000 Feb 15;1(2):28-41. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2000. PMID: 12167888 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Storage in Distilled Water for Three Months on the Antimicrobial Properties of Poly(methyl methacrylate) Denture Base Material Doped with Inorganic Filler.Materials (Basel). 2016 Apr 29;9(5):328. doi: 10.3390/ma9050328. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28773451 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the growth of dental plaque on the surfaces of removable orthodontic aligners after the use of different cleaning methods.Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2015 Dec 15;7:125-31. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S95814. eCollection 2015. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2015. PMID: 26719726 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of zinc oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposites on the cytotoxicity, antibacterial and mechanical properties of polymethyl methacrylate.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):1013. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04754-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39210376 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of antifungal activity of home-generated ozonated water on Candida albicans.Curr Med Mycol. 2018 Jun;4(2):27-31. doi: 10.18502/cmm.4.2.67. Curr Med Mycol. 2018. PMID: 30324154 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for Preventing and Treating Oral Mucosal Infections Associated with Removable Dentures: A Scoping Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;13(3):273. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030273. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambjørnsen E, Rise J. The effect of verbal information and demonstration on denture hygiene in elderly people. Acta Odontol Scand. 1985;43:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Ambjørnsen E, Valderhaug J, Norheim PW, Fløystrand F. Assessment of an additive index for plaque accumulation on complete maxillary dentures. Acta Odontol Scand. 1982;40:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Andrucioli MCD, Macedo LD, Panzeri H, Lara EHG, Paranhos HF. Comparison of two cleansing pastes for the removal of biofilm from dentures and palatal lesions in patients with atrophic chronic candidiasis. Braz Dent J. 2004;15:220–224. - PubMed
-
- Augsburger RH, Elahi JM. Evaluation of seven proprietary denture cleansers. J Prosthet Dent. 1982;47:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Chan ECS, Iugovaz I, Siboo R, Bilyk M, Barolet R, Amsel R, et al. Comparison of two popular methods for removal and killing of bacteria from dentures. J Can Dent Assoc. 1991;57:937–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources