Role of spatial ionic distribution on the energetics of hydrophobic assembly and properties of the water/hydrophobe interface
- PMID: 22231014
- PMCID: PMC4211274
- DOI: 10.1039/c1cp20839j
Role of spatial ionic distribution on the energetics of hydrophobic assembly and properties of the water/hydrophobe interface
Abstract
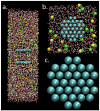
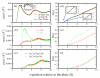
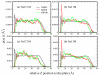
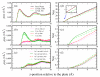
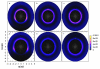
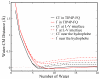
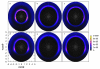
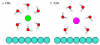
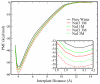
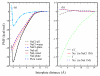
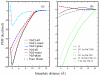
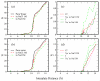
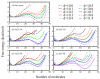
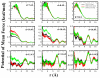
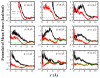
We present results from all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of large-scale hydrophobic plates solvated in NaCl and NaI salt solutions. As observed in studies of ions at the air-water interface, the density of iodide near the water-plate interface is significantly enhanced relative to chloride and in the bulk. This allows for the partial hydration of iodide while chloride remains more fully hydrated. In 1 M solutions, iodide directly pushes the hydrophobes together (contributing -2.51 kcal mol(-1)) to the PMF. Chloride, however, strengthens the water-induced contribution to the PMF by ~-2.84 kcal mol(-1). These observations are enhanced in 3 M solutions, consistent with the increased ion density in the vicinity of the hydrophobes. The different salt solutions influence changes in the critical hydrophobe separation distance and characteristic wetting/dewetting transitions. These differences are largely influenced by the ion-specific expulsion of iodide from bulk water. Results of this study are of general interest to the study of ions at interfaces and may lend insight to the mechanisms underlying the Hofmeister series.
Figures
References
-
- Frolov AI, Rozhin AG, Fedorov MV. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2010;11:2612–2616. - PubMed
-
- Lin S, Blankschtein D. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2010;2010:15616–15625. - PubMed
-
- Zelada-Guillen GA, Riu J, Duzgun A, Rius FX. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009;48:7334–7337. - PubMed
-
- Zelada-Guillen GA, Riu J, Duzgun A, Rius FX. Angew. Chem. 2009;121:7470–7473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

