Mapping the regulatory sequences controlling 93 breast cancer-associated miRNA genes leads to the identification of two functional promoters of the Hsa-mir-200b cluster, methylation of which is associated with metastasis or hormone receptor status in advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 22231446
- PMCID: PMC3448136
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.584
Mapping the regulatory sequences controlling 93 breast cancer-associated miRNA genes leads to the identification of two functional promoters of the Hsa-mir-200b cluster, methylation of which is associated with metastasis or hormone receptor status in advanced breast cancer
Abstract
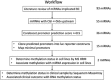
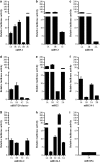
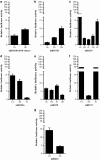
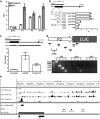
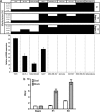
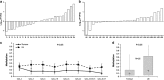
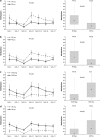
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs of ∼20 nt in length that are capable of modulating gene expression post-transcriptionally. Although miRNAs have been implicated in cancer, including breast cancer, the regulation of miRNA transcription and the role of defects in this process in cancer is not well understood. In this study we have mapped the promoters of 93 breast cancer-associated miRNAs, and then looked for associations between DNA methylation of 15 of these promoters and miRNA expression in breast cancer cells. The miRNA promoters with clearest association between DNA methylation and expression included a previously described and a novel promoter of the Hsa-mir-200b cluster. The novel promoter of the Hsa-mir-200b cluster, denoted P2, is located ∼2 kb upstream of the 5' stemloop and maps within a CpG island. P2 has comparable promoter activity to the previously reported promoter (P1), and is able to drive the expression of miR-200b in its endogenous genomic context. DNA methylation of both P1 and P2 was inversely associated with miR-200b expression in eight out of nine breast cancer cell lines, and in vitro methylation of both promoters repressed their activity in reporter assays. In clinical samples, P1 and P2 were differentially methylated with methylation inversely associated with miR-200b expression. P1 was hypermethylated in metastatic lymph nodes compared with matched primary breast tumours whereas P2 hypermethylation was associated with loss of either oestrogen receptor or progesterone receptor. Hypomethylation of P2 was associated with gain of HER2 and androgen receptor expression. These data suggest an association between miR-200b regulation and breast cancer subtype and a potential use of DNA methylation of miRNA promoters as a component of a suite of breast cancer biomarkers.
Figures


References
-
- Rapid amplification of 5′ complementary DNA ends (5′ RACE) Nat Methods. 2005;2:629–630. - PubMed
-
- Bartels CL, Tsongalis GJ. MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem. 2009;55:623–631. - PubMed
-
- Boyd SD. Everything you wanted to know about small RNA but were afraid to ask. Lab Invest. 2008;88:569–578. - PubMed
-
- Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7846–7854. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

