De novo assembly and genotyping of variants using colored de Bruijn graphs
- PMID: 22231483
- PMCID: PMC3272472
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1028
De novo assembly and genotyping of variants using colored de Bruijn graphs
Abstract
Detecting genetic variants that are highly divergent from a reference sequence remains a major challenge in genome sequencing. We introduce de novo assembly algorithms using colored de Bruijn graphs for detecting and genotyping simple and complex genetic variants in an individual or population. We provide an efficient software implementation, Cortex, the first de novo assembler capable of assembling multiple eukaryotic genomes simultaneously. Four applications of Cortex are presented. First, we detect and validate both simple and complex structural variations in a high-coverage human genome. Second, we identify more than 3 Mb of sequence absent from the human reference genome, in pooled low-coverage population sequence data from the 1000 Genomes Project. Third, we show how population information from ten chimpanzees enables accurate variant calls without a reference sequence. Last, we estimate classical human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotypes at HLA-B, the most variable gene in the human genome.
Figures
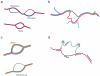
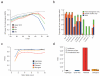


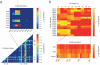
References
-
- Li R, Li Y, Kristiansen K, Wang J. SOAP: short oligonucleotide alignment program. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:713–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

