Genomic analyses of modern dog breeds
- PMID: 22231497
- PMCID: PMC3559126
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-011-9387-6
Genomic analyses of modern dog breeds
Abstract
A rose may be a rose by any other name, but when you call a dog a poodle it becomes a very different animal than if you call it a bulldog. Both the poodle and the bulldog are examples of dog breeds of which there are >400 recognized worldwide. Breed creation has played a significant role in shaping the modern dog from the length of his leg to the cadence of his bark. The selection and line-breeding required to maintain a breed has also reshaped the genome of the dog, resulting in a unique genetic pattern for each breed. The breed-based population structure combined with extensive morphologic variation and shared human environments have made the dog a popular model for mapping both simple and complex traits and diseases. In order to obtain the most benefit from the dog as a genetic system, it is necessary to understand the effect structured breeding has had on the genome of the species. That is best achieved by looking at genomic analyses of the breeds, their histories, and their relationships to each other.
Figures

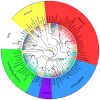
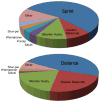
References
-
- Alderton D. Dogs. New York: Dorling Kindersley, Ltd; 2002.
-
- American Kennel Club. The Complete Dog Book. 19. New York, NY: Howell Book House; 1998. Revised ed.
-
- American Veterinary Medical Association. US Pet Ownership and Demographics Sourcebook. 1. Schaumburg, ILL: American Veterinary Medical Association; 2002.
-
- Awano T, Johnson GS, Wade CM, Katz ML, Johnson GC, Taylor JF, Perloski M, Biagi T, Baranowska I, Long S, March PA, Olby NJ, Shelton GD, Khan S, O’Brien DP, Lindblad-Toh K, Coates JR. Genome-wide association analysis reveals a SOD1 mutation in canine degenerative myelopathy that resembles amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:2794–2799. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

