The neuroimmune guidance cue netrin-1 promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting the emigration of macrophages from plaques
- PMID: 22231519
- PMCID: PMC3262880
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2205
The neuroimmune guidance cue netrin-1 promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting the emigration of macrophages from plaques
Abstract
Atherosclerotic plaque formation is fueled by the persistence of lipid-laden macrophages in the artery wall. The mechanisms by which these cells become trapped, thereby establishing chronic inflammation, remain unknown. Here we found that netrin-1, a neuroimmune guidance cue, was secreted by macrophages in human and mouse atheroma, where it inactivated the migration of macrophages toward chemokines linked to their egress from plaques. Acting via its receptor, UNC5b, netrin-1 inhibited the migration of macrophages directed by the chemokines CCL2 and CCL19, activation of the actin-remodeling GTPase Rac1 and actin polymerization. Targeted deletion of netrin-1 in macrophages resulted in much less atherosclerosis in mice deficient in the receptor for low-density lipoprotein and promoted the emigration of macrophages from plaques. Thus, netrin-1 promoted atherosclerosis by retaining macrophages in the artery wall. Our results establish a causative role for negative regulators of leukocyte migration in chronic inflammation.
Figures
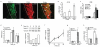
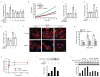
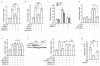
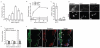
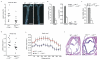
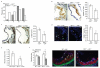
Comment in
-
The ins and outs of inflammatory cells in atheromata.Cell Metab. 2012 Feb 8;15(2):135-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.01.012. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22326216
References
-
- Libby P, Aikawa M. Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: new mechanisms and clinical targets. Nat Med. 2002;8:1257–1262. - PubMed
-
- Bellingan GJ, Caldwell H, Howie SE, Dransfield I, Haslett C. In vivo fate of the inflammatory macrophage during the resolution of inflammation: inflammatory macrophages do not die locally, but emigrate to the draining lymph nodes. J Immunol. 1996;157:2577–2585. - PubMed
-
- Rong JX, et al. Elevating high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice remodels advanced atherosclerotic lesions by decreasing macrophage and increasing smooth muscle cell content. Circulation. 2001;104:2447–2452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

