Vertical nanowire electrode arrays as a scalable platform for intracellular interfacing to neuronal circuits
- PMID: 22231664
- PMCID: PMC4209482
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2011.249
Vertical nanowire electrode arrays as a scalable platform for intracellular interfacing to neuronal circuits
Abstract
Deciphering the neuronal code--the rules by which neuronal circuits store and process information--is a major scientific challenge. Currently, these efforts are impeded by a lack of experimental tools that are sensitive enough to quantify the strength of individual synaptic connections and also scalable enough to simultaneously measure and control a large number of mammalian neurons with single-cell resolution. Here, we report a scalable intracellular electrode platform based on vertical nanowires that allows parallel electrical interfacing to multiple mammalian neurons. Specifically, we show that our vertical nanowire electrode arrays can intracellularly record and stimulate neuronal activity in dissociated cultures of rat cortical neurons and can also be used to map multiple individual synaptic connections. The scalability of this platform, combined with its compatibility with silicon nanofabrication techniques, provides a clear path towards simultaneous, high-fidelity interfacing with hundreds of individual neurons.
Figures
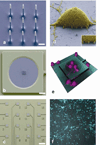
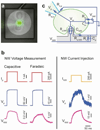
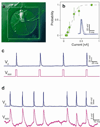
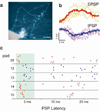
Comment in
-
A 'nano' era for electrophysiology.Nat Methods. 2012 Apr;9(4):321. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1961. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22563598 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pine J. Advances in Network Electrophysiology. 2006:3–23.
-
- Molleman A. Patch clamping. John Wiley and Sons: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

