Recent advances in stealth coating of nanoparticle drug delivery systems
- PMID: 22231928
- PMCID: PMC3288878
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.1157
Recent advances in stealth coating of nanoparticle drug delivery systems
Abstract
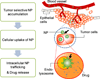
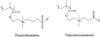
Modifying surfaces of nanoparticles (NPs) with polyethylene glycol (PEG), the so-called PEGylation, is the most commonly used method for reducing premature clearance of NPs from the circulation. However, several reports point out that PEGylation may negatively influence the performance of NPs as a drug carrier. Alternative surface modification strategies, including substitute polymers, conditional removal of PEG, and biomimetic surface modification, may provide solutions for the limitations of PEG.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Peer D, Margalit R. Fluoxetine and reversal of multidrug resistance. Cancer Letters. 2006;237:180–187. - PubMed
-
- Luqmani YA. Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Medical Principles and Practice. 2005;14:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Kuo T-C, Lu H-P, Chao CCK. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor sorafenib sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to taxol by suppressing the HURP protein. Biochemical Pharmacology. 2011;82:184–194. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Clinical Applications of Research on Angiogenesis. New England Journal of Medicine. 1995;333:1757–1763. - PubMed
-
- Eddy HA, Casarett GW. Development of the vascular system in the hamster malignant neurilemmoma. Microvascular Research. 1973;6:63–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

