The influence of the polar head and the hydrophobic chain on the skin penetration enhancement effect of poly(ethylene glycol) derivatives
- PMID: 22232021
- PMCID: PMC3299471
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-011-9745-4
The influence of the polar head and the hydrophobic chain on the skin penetration enhancement effect of poly(ethylene glycol) derivatives
Abstract
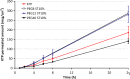
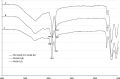
The effect of a homologue series of nonionic surfactants, namely poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) fatty acid esters, differing in oxyethylene (PEG 8, PEG 12, and PEG 40) and fatty acid (stearate, mono and di-laurate, and mono and di-oleate) chain lengths, on in vitro skin permeability of ketoprofen (KTP) vehicled in plasters was investigated. The drug diffusion through hairless mouse skin as well as the effect of the surfactant type and strength was studied by Franz diffusion cells and ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. The use of PEG stearate series revealed that the surfactant with the largest polar head, namely PEG 40, was ineffective in enhancing the skin permeation of KTP, independently of the plaster concentrations. The effect of the hydrophobic chain was investigated only by using the shortest oxyethylene chains. The experimental results revealed that the oxyethylene chain length of surfactants appeared to be more influent than the alkyl chain. The prediction of the absorption enhancing capability of these PEG derivatives appeared related to the vehicle other than the proper combination of the number of ethylene oxide groups and alkyl groups.
Figures
References
-
- Florence T, Tucker IG, Walters KA. Interactions of nonionic alkyl and aryl ethers with membranes and other biological systems. In: Rosen MJ, editor. Structure: performance relationships in surfactants. ACS Symp. Ser; 1984; 253 p. 189–207
-
- Breuer MM. The interaction between surfactant and keratinous tissue. J Soc Cosmet Chem. 1979;30:41–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous