Activation of legumain involves proteolytic and conformational events, resulting in a context- and substrate-dependent activity profile
- PMID: 22232165
- PMCID: PMC3253828
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309111048020
Activation of legumain involves proteolytic and conformational events, resulting in a context- and substrate-dependent activity profile
Abstract
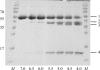
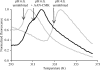
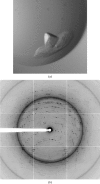
Localized mainly to endo/lysosomes, legumain plays an important role in exogenous antigen processing and presentation. The cysteine protease legumain, also known as asparaginyl endopepetidase AEP, is synthesized as a zymogen and is known to undergo pH-dependent autoproteolytic activation whereby N-terminal and C-terminal propeptides are released. However, important mechanistic details of this pH-dependent activation as well as the characteristic pH activity profile remain unclear. Here, it is shown that all but one of the autocatalytic cleavage events occur in trans, with only the release of the C-terminal propeptide being relevant to enzymatic activity. An intriguing super-activation event that appears to be exclusively conformational in nature and enhances the enzymatic activity of proteolytically fully processed legumain by about twofold was also found. Accepting asparagines and, to lesser extent, aspartic acid in P1, super-activated legumain exhibits a marked pH dependence that is governed by the P1 residue of its substrate and conformationally stabilizing factors such as temperature or ligands. The crystallization and preliminary diffraction data analysis of active legumain are presented, which form an important basis for further studies that should clarify fundamental aspects of activation, activity and inactivation of legumain, which is a key target in (auto-)immunity and cancer.
© 2012 International Union of Crystallography. All rights reserved.
Figures

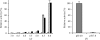


References
-
- Adams, P. D., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Hung, L.-W., Ioerger, T. R., McCoy, A. J., Moriarty, N. W., Read, R. J., Sacchettini, J. C., Sauter, N. K. & Terwilliger, T. C. (2002). Acta Cryst. D58, 1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Alim, M. A., Tsuji, N., Miyoshi, T., Islam, M. K., Huang, X., Hatta, T. & Fujisaki, K. (2008). J. Insect Physiol. 54, 573–585. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Fernandez, M., Barrett, A. J., Gerhartz, B., Dando, P. M., Ni, J. & Abrahamson, M. (1999). J. Biol. Chem. 274, 19195–19203. - PubMed
-
- Baker, D., Shiau, A. K. & Agard, D. A. (1993). Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 5, 966–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

