Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic studies of NahF, a salicylaldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida G7 involved in naphthalene degradation
- PMID: 22232182
- PMCID: PMC3253845
- DOI: 10.1107/S174430911105038X
Expression, purification and preliminary crystallographic studies of NahF, a salicylaldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas putida G7 involved in naphthalene degradation
Abstract
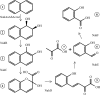
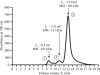
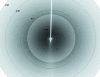
Pseudomonas putida G7 is one of the most studied naphthalene-degrading species. The nah operon in P. putida, which is present on the 83 kb metabolic plasmid NAH7, codes for enzymes involved in the conversion of naphthalene to salicylate. The enzyme NahF (salicylaldehyde dehydrogenase) catalyzes the last reaction in this pathway. The nahF gene was subcloned into the pET28a(TEV) vector and the recombinant protein was overexpressed in Escherichia coli Arctic Express at 285 K. The soluble protein was purified by affinity chromatography followed by gel filtration. Crystals of recombinant NahF (6×His-NahF) were obtained at 291 K and diffracted to 2.42 Å resolution. They belonged to the hexagonal space group P6(4)22, with unit-cell parameters a = b = 169.47, c = 157.94 Å. The asymmetric unit contained a monomer and a crystallographic twofold axis generated the dimeric biological unit.
© 2012 International Union of Crystallography. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Arun, A., Raja, P. P., Arthi, R., Ananthi, M., Kumar, K. S. & Eyini, M. (2008). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 151, 132–142. - PubMed
-
- Bosch, R., García-Valdés, E. & Moore, E. R. (1999). Gene, 236, 149–157. - PubMed
-
- Carneiro, F. R., Silva, T. C., Alves, A. C., Haline-Vaz, T., Gozzo, F. C. & Zanchin, N. I. (2006). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 343, 260–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

